ADDRESS TO THE READERS
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
There is a contradiction between the need of teachers of internal medicine departments in the methodology for communicative competence (CC) of general practitioners in brief preventive counseling and the lack of evidence-based classes on CC formation in brief preventive counseling.
The existing contradiction made it possible to identify the research problem — the need to develop a methodology for the development of CC of general practitioners in brief preventive counseling.
In the context of the problem, the study aim was determined — to define the methodological features of CC formation in the general practitioner in brief preventive counseling.
To achieve this goal, the following research methods were used: theoretical: theoretical analysis of philosophical, pedagogical, psychological and methodological literature; designing the educational process; experimental: direct and indirect pedagogical observation, pedagogical experiment, questioning, control sections.
The methodological features of CC formation are the simultaneous development of the intellectual and emotional fields of the doctor’s personality (communication skills in conducting all stages of brief preventive counseling) and the volitional field of the doctor’s personality (belief in the need to master the CC of doctor-patient interaction).
The method of doctor’s CC development is based on the technology of educational training. The content of the training is a system of three following components: cognitive component — knowledge of the regulatory framework for conducting brief preventive counseling; knowledge about the criteria for its effectiveness; features of the management and principles of implementation; emotional and motivational component — the formation of personally significant ideas about oneself as a subject of professional communication in the process of brief preventive counseling; the behavioral component is the formation of the doctor’s beliefs in the need to master communicative skills that ensure the formation of competence in brief preventive counseling.
The results of its experimental implementation for the formation of a doctor CC showed a high level of development: skills in conducting all stages of brief preventive counseling; beliefs in the need for the doctor to master the CC of doctor-patient interaction.
The article is devoted to the study of social attractiveness of Russian higher medical education for foreign students. The importance of promotion of educational services of Russian universities is highlighted. Criteria for choosing a university by foreign students were assessed. The importance of modern and effective communication channels of the university and foreign applicants, modern infrastructure and learning technologies was determined. The work contains recommendations for improving the attractiveness of medical universities for foreigners.
- The occurrence of mental illness manifestations (symptoms of emotional burnout and neuroticism) was determined and their relationship with emotional intelligence in a group of medical workers was identified.
- The system of emotional competencies based on factor analysis of self-regulation, empathy, reflection and emotional intelligence was empirically identified and described.
- The protective role of intrapersonal and interpersonal emotional competencies with a mature regulatory component of behavior and activity in maintaining the mental health of medical workers
Aim. To study the protective role of emotional competencies (ECs) in maintaining the mental health of medical workers.
Material and methods. The sample consisted of 170 medical workers. Methods for assessing the level of emotional burnout and empathic abilities by V. V. Boyko, emotional intelligence by D. V. Lyusin, the style of behavior self-regulation by V. I. Morosanova, the differential type of reflection by D. A. Leontiev, the neuroticism by K. K. Yakhin, D. M. Mendelevich. The following statistical methods were used: correlation analysis (Pearson r-test), hierarchical factor analysis.
Results. Reliable two-way correlations were determined between a wide range of individual symptoms of emotional burnout and neuroticism, which are manifestations of mental illness, and the characteristics of the emotional intelligence of medical workers. Based on factor analysis of self-regulation parameters, empathy, reflection and emotional intelligence, 4 ECs were identified: intrapersonal areflexive Ego-centered, intrapersonal infantile, regulative, intrapersonal reflexive. We determined that in mentally healthy medical workers, the regulative ECs are most pronounced. Employees with the early stage mental illness simultaneously present intrapersonal ECs that are multidirectional in terms of reflexivity (areflexive Ego-centered and reflexive). Mentally unhealthy medical workers were found to be unformed in all ECs.
Conclusion. The positive relationships identified in the study between regulative mature intrapersonal and interpersonal ECs and a favorable mental health of medical workers suggest the need to develop training programs for ECs as a factor in maintaining the mental health of medical workers.
Technological advances in the modern world have led to a paradigm shift in medical education, identifying new challenges. The need to meet these challenges has required the implementation of evidence-based clinical practice, which allows the best quality evidence to be used to provide optimal patient care and improve healthcare efficiency. Obtaining evidence of the efficacy and safety of drugs and medical technologies, the diagnostic accuracy of interventions became possible due to the introduction of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. This methodology forms clinical thinking in parallel with the development of research and analytical competencies, which is one of the urgent tasks of modern medical education. The article reflects the experience of the Department of Internal Diseases of the Sechenov University in implementing a practice-oriented research module aimed at developing critical thinking using evidence-based medicine methods among students and residents. The inclusion of research competencies in the educational process will make it possible to qualitatively transform medical education and form a generation of competitive competent specialists in demand in the world of constantly developing technologies.
The article is devoted to the study of the place of history subjects in the formation of general cultural competencies of medical students. A theoretical analysis of the topic in domestic and foreign history and pedagogical science has been carried out. The necessity of history subjects in the system of higher professional medical education is substantiated. Based on many years of experience, pedagogical technologies developed by the authors are presented that most fully form general cultural and professional competencies within historical subjects. The data of pedagogical research on the topic are given, the opinions of students on the content of history subjects, on the process of forming knowledge, skills and abilities of medical students are explicated. The practical significance of the study for improving the pedagogical process in a medical university is reflected.
ОРГАНИЗАЦИЯ ЗДРАВООХРАНЕНИЯ
Aim. To identify problems in the management of preventive examinations in remote areas, using the example of the Khvoininsky district of the Novgorod Oblast and ways to improve it. The article reveals the problems of managing preventive measures in the regions of the Russian Federation, remote from the regional center.
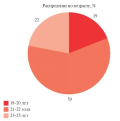
Material and methods. Observations and experience of preventive measures carried out by the staff of St. Petersburg State Pediatric Medical University within the "University — Region" project, data from electronic medical records of 178 patients were used.
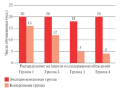
Results. A high proportion of loss to follow-up was noted — 99 out of 278 (36%). The bulk was patients over 40 years old, who were assigned to health group IIIa. The difficulty of conducting medical examinations in a sparsely populated area is associated with insufficient awareness of the population, combined with low interest, a shortage of specialists, untimely necessary studies, a significant bureaucratic work, unstable Internet connection, and insufficient cancer awareness among medical workers.
Conclusion. Expanding the promotion and information component of preventive measures, increasing patient focus, combining the first and second stages of clinical examination into one with subsequent convenient routing of patients, introducing telemedicine technologies and portable diagnostic complexes, improving the professional knowledge and competencies of primary care physicians — all these activities are aimed at improving coverage of population, increasing the adherence of patients with effective medical follow-up.
OPINION ON A PROBLEM
Aim. To identify problems of domestic natural science education and patriotism promotion (as a motivational personality component), which negatively affect the professional training of health professionals.
Material and methods. When working on the article, we used the following methods: theoretical — analysis of modern legal documents of secondary general education, analysis of recommended educational literature on subjects, and empirical — analysis of the experience of biology teachers in modern conditions according to the recommended programs of disciplines and standards; analysis of the results of the Unified State Exam (USE) for 2021-2022 and scientific generalization.
Results. An analysis of the main problems of natural science education at the present time is presented. The authors consider the most significant of them to be a change in the content of school education, an unacceptable reduction in hours for natural science disciplines, ignoring the domestic tradition and didactic principles of science and systematization, practical experience accumulated by domestic teachers and methodologists in the preparation of programs and textbooks. The reasons for the lack of special knowledge and objective thinking in a large part of students are considered, which is confirmed by the USE for the period 2015-2022. It is pointed out that it is practically impossible to carry out a systematic mastering of the content of an educational subject and the development of mental skills, based on modern textbooks. The combination of these problems has led to a decrease in the development and educational potential of the natural sciences and the quality of education in general.
Conclusion. The article suggests possible ways to overcome this undesirable trend, substantiates the need to rethink the importance of school science education as a resource for the development of science, the national economy, medicine and the defense industry. There is a need to create an "image of the future" among students as a system-forming factor in the social and cultural development of Russian society.
The article describes the formation of social communication (SC) skills among healthcare professionals in order to determine its place in professional activities.
A theoretical analysis of the philosophical, pedagogical, psychological and scientific-methodical literature related to the problem under study was carried out. The national pedagogical experience in SC development was analyzed through the prism of cultural and moral patterns embedded in the national literature. The following methods were used: conversations with students, medical workers, discussion, survey.
According to the authors, the low interest in national literature and culture is a significant reason for the low level of SC skills among workers in the social and medical service and in professional group communication. A survey among students showed a low interest in the national cultural samples, including those expressed in national literature.
According to the authors, in the development of SC skills in future healthcare professionals, the experience of domestic pedagogy is of great importance, aimed at improving the moral education necessary for adequate behavior and communication, not only in the context of local and national realities, but also including respect for other cultures.
At present, additional courses are increasingly being introduced into the postgraduate medical education program, which contain discussions on the personal qualities of a doctor and the functions of the medical profession. To that end, certain moral and ethical reference points are selected from the biographies of physicians of the "past", which are elevated to an ideal and repeated in every biographical article without proper professional evaluation. There is a mythologization of the image of a doctor among the professional community and the reason for this trend, in part, lies in the false idea that the history of medicine can be written without specialized knowledge and without the tools that historians use when analyzing biographical information.
The article provides a general overview of the development of medical knowledge, which was influenced not only by political and economic, but also by religious factors. A specialized approach used by historians in the analysis of biographical information is considered. A different view is offered on the potential of interpreting the image of a doctor, evaluating the activities of physicians of the past and forming examples for doctors of the future that would be in demand in modern professional education.
ИСТОРИЯ НАУЧНО-ПЕДАГОГИЧЕСКИХ ШКОЛ
Semen Semenovich Zimnitsky is an outstanding Russian internist of the early XX century. He created a functional direction and made a significant contribution to internal medicine, infectiology, immunology and microbiology, but his studies of gastroenterology are fundamental. The Zimnitsky’s works on hepatology, pancreatic diseases, and balneology are interesting. S. S. Zimnitsky discovered 5 types of gastric secretion, which turned out to be reversible, and proposed a repeated breakfast. The pinnacle of his work is Zimnitsky’s test, which makes it possible to determine the renal function without resorting to any invasive procedures and in no way burdening the patient. The onset of test creation was laid by S. S. Zimnitsky in his doctoral dissertation devoted to gastroenterology.
The pinnacle of S. S. Zimnitsky scientific heritage is the Zimnitsky, which makes it possible to assess the renal function without invasive procedures and burdening the patient. Proposed a hundred years ago, the Zimnitsky test shows its effectiveness at the present time. S. S. Zimnitsky proposed an original classification of hydronephrosis, described a special form of nephritis and rejected the filtration theory of urine formation, promoting the secretory one. In his purely scientific nephrological articles, S. S. Zimnitsky acts as a sincere and ardent patriot of his great homeland.
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)