ADDRESS TO THE READERS
УПРАВЛЕНИЕ ПРОФЕССИОНАЛЬНЫМ ОБРАЗОВАНИЕМ
The article examines the implementation of the principle of educational space unity, ensuring the quality of education throughout the Russia. We also describe the interdependence of practical health care needs for primary care specialists capable of providing high-quality primary care and the functions of an integrated system of a unified educational space for internists and general practitioners (family doctors) (GPs) focused on the social order.
Aim. To analyze the conceptual foundations of the system of a unified educational space for internists and GPs (family doctors) as ways to improve the quality of training of specialists.
Material and methods. The following were used in this study: analysis of educational trends in the modern world and medical education in particular; structural and functional analysis in the study of legislation regulating the training of internists and GPs (family doctors); a system approach that defines the components of a unified educational space for in ternists and GPs (family doctors); a method for predicting changes in the de velopment of a unified educational space for internists and GPs (family doctors).
Results. Having considered the potential capabilities of a unified educational space for internists and GPs (family doctors), the following were revealed: regulatory, social, educational, managerial factors influencing the training of internists and GPs (family doctors) were identified; strategies for the development of a unified educational space for internists and GPs (family doctors) were determined at the level of goals, content, processes, and results; the relationship between the training of internists and GPs (family doctors) and the needs of practical healthcare was established; the internal components and functions of a unified educational space for internists and GPs (family doctors) have been identified and substantiated, and the framework factors have been defined. A theoretical model of a unified educational space for internists and GPs (family doctors) has been created, including external factors, target, motivational, design, content, managerial and evaluative components, as well as planned results, manifested in the functions.
Conclusion. To summarize, we can state the following: for effective and high-quality management training of internists and GPs (family doc tors), a unified educational space is of paramount importance, this will make it possible to preserve the best traditions of the country's therapeutic school and its future development.
PEDAGOGY OF DEVELOPMENT AND COOPERATION
- The range of questions that received the maximum number of positive answers from modern students, reflecting the high level of their civic identity and self-awareness, was determined.
- A detailed analysis of those questions in the questionnaire was carried out.
- The questionnaire developed by the author and tested during an experimental study has practical value in diagnosing the characteristics of the civic consciousness of modern students at the present stage of development of society and educational systems.
Aim. To study the features of civic consciousness among modern university students.
Material and methods. A total of 467 students took part in the study. The original author’s questionnaire was used (I. V. Koltsova, 2024), aimed at identifying the characteristics of students’ civic consciousness.
Results. The study showed that the majority of students believe that secondary schools should take an active part in the development of civic consciousness of young people. Students behave in society in accordance with generally accepted rules, know the history of the Russian Federation, its traditions and customs, conspicuous figures, rights and responsibilities, speak their native language and actively use it in communication with representatives of their nationality. After training, most graduates plan to stay and work in the Russian Federation. However, about 30% of subjects have low scores on such issues as participation in the Russian presidential and legislative elections. There is a high awareness on socio-political events and laws, which indicates the low social activity of this group of respondents.
Conclusion. The conducted research made it possible to identify both positive trends in relation to the civic consciousness of students, as well as problem areas that require targeted educational work.
Aim. The article is devoted to the analysis of personalized training through the lens of the mentoring system at a medical university.
Material and methods. The study involved 211 full-time 1st-6th year students of the Volgograd State Medical University. A sociological survey was used in the form of a questionnaire.
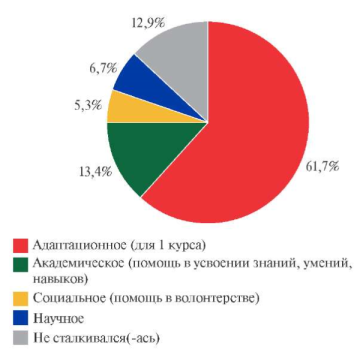
Results. The article reveals the role of mentoring within federal innovation platform System of Personalized Training in a Higher Education Establishment. The authors substantiate the need to introduce a mentoring model to optimize the educational process and unlock the potential of students, residents, and teachers. The article examines the conceptual foundations, goals and objectives of mentoring, as well as implementation arrangements within the federal innovation platform. Additionally, the mentoring model benefits presented, including improved academic performance, increased student motivation, professional skill development, and career counseling. It also emphasizes the importance of monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the mentoring model to ensure its continuous modernization.
Conclusion. The article emphasizes that the introduction of a mentoring model in the federal innovation platform System of Personalized Training in a Higher Education Establishment is an important step to achieve the goals of personalized training. The authors recommend future research on the implementation and evaluation of mentoring models in different higher education contexts.
The article analyzes the results of the All-Russian competition for general practitioners, family doctors and internists held over five years by the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine with the support of the Russian Society for the Prevention of Non communicable Diseases.
Aim. To determine the methodological characteristics of managing the academic competition as a type of informal education.
Material and methods. To conduct the competition, practice-oriented tasks corresponding to professional tasks of a general practitioner were developed. In addition, we developed an original questionnaire to assess the impact of participation in the academic competition on the professional development. Family doctors and general practitioners with 1-10 years of experience, as well as internists, were included.
Results. The methodological characteristics of the academic competition management as a type of informal education were determined: practice-oriented goals aimed at improving the knowledge, skills and abilities, competencies of the participants; the content of tasks based on the theory-practice relationship; compliance of tasks and real situations in the practice of a general practitioner; a systematic approach to competition management. Conclusion. The effectiveness of the academic competition as a type of informal education contributes to the professional development of participants, promotes the development of long-term attitudes towards improving professional knowledge, skills, abilities and competencies necessary for solving professional problems.
EVIDENCE-BASED PEDAGOGY
The functional responsibilities of general practitioners (family doctors) (GPs) have changed significantly over the past decade. The number of GP functions has expanded. Despite the increasingly complex professional activities of GPs, there is no scientific evidence for the qualification characteristics of GPs expressed in knowledge, skills, abilities, and competencies in the theory and practice in training. In this regard, a study was conducted to determine the priority of GP competencies that make up the qualification characteristics of a specialist. Aim. To analyze, generalize and rationale the research results, as well as to develop preliminary guidelines for GP training. Material and methods. The information base for the study was the results of ranking competencies according to their importance in the professional activities of GPs in Russia. It was obtained during the ascertaining experiment, implemented using the Delphi method as a method of expert assessment and strategic planning of training specialists. Conclusion. The analysis of competencies developed and agreed upon by experts showed its compliance with the job functions of GPs, the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard for the General Medical Practice (Family Medicine) and the WONCA guidelines. A summary of the study results to determine the priority of competence in GP activities showed the following: — all competencies (25) were defined as necessary and constitutive of GP qualification; — 21 competencies were considered significant and highly significant for GPs; — 4 competencies were considered as of moderate significance and below moderate significance. The analysis of the priority of competences revealed insufficient methodological support for GP training in accordance with the social order. The results obtained showed the need to continue the study within the project "Quality Management of Training of General Practitioners (Family Doctors)".
Aim. To study the effectiveness of a virtual pharmacy as an element of an electronic information educational environment at the Department of Pharmacology.
Material and methods. A total of 250 3rd year students of the Faculty of General Medicine and 196 2nd year students of the Faculty of Dentistry of the First Pavlov State Medical University of St. Petersburg. To achieve these goals, structured interviews, focus groups, and subsequent analysis were used. The performance of third-year students at the Faculty of General Medicine was assessed before and after the introduction of digital tools for visualizing material using elements of a virtual pharmacy.
Results. A survey of students found high interest in using visual methods and, in particular, a virtual pharmacy. Clinical and pharmacological tasks using a virtual pharmacy significantly facilitated the acquisition of pharmacological knowledge and were rated positively by the majority of students. An analysis of the academic success of students who with a virtual pharmacy resource found that the average score increased and they began to pass the tests on the first try. When collecting data, Google forms were used, which, due to anonymity, made it possible to receive detailed proposals from students for improving the virtual pharmacy and teaching methods using the electronic information educational environment.
Conclusion. The study showed that the virtual pharmacy method has established itself as an effective pedagogical tool that has made it possible to increase the visibility of difficult educational material and the efficiency of learning new knowledge.
NEWS FROM THE MEETING OF STATE DEPARTMENTS OF THERAPY
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)