ADDRESS TO THE READERS
PEDAGOGY OF DEVELOPMENT AND COOPERATION
The training of medical specialists needs systemic transformation. Educational organizations must create conditions for developing research competencies and innovative activities among future healthcare, as well as implement transversal formats for attracting and managing talented youth at all stages of professional development. To create a passport of educational program competencies and describe the results of educational activities, the "Competency Standard" database has been developed. The aim was to classify groups and categories of competencies, including the subject’s competencies (both educational and project), the competencies of activity development, and transversal competences applicable in any type of educational and project activities. Project-based training for students makes it possible to form following priority competencies in medicine and pharmacy: analytical, research, professional, communicative, digital, managerial and entrepreneurial. Project-based learning and new educational formats are used as an transversal technology in the implementation of innovative programs, the target audience of which is students with increased educational potential, claiming a portfolio of high-quality competencies.
Aim. To develop a patient education algorithm used by medical workers. The leading method for studying this problem is a pedagogical experiment, as well as a statistical processing of quantitative research results. The relevance of this study is due to the need to address the priorities of the Healthcare national project, i.e. developing the skills of maintaining a healthy lifestyle among the population, changing behavior and attitudes towards their own health and the health of others. The introduction of educational programs for patients in combination with therapeutic measures contributes to the most complete rehabilitation. Forming partnerships and trust between patients and medical workers to prevent diseases requires the latter to have psychological and pedagogical knowledge and skills.
Material and methods. The study was conducted on the basis of the City Outpatient Clinic № 7 (Kazan). The study was conducted in the Department of Internal Medicine on the daytime basis. The experiment involved 20 nurses, 15 doctors and 60 patients from these departments. The study was carried out in three following stages: at the first stage, the current state of the problem under study in pedagogical theory and practice was analyzed, a research methodology program was developed, and a survey of nurses at the medical institution was conducted. At the second stage, the theoretical concept of the study was adjusted, a training experiment was conducted with doctors and senior nurses, and a structural and functional model of pedagogical training of medical workers for patient education was introduced. At the third stage, analysis, generalization and systematization of the data obtained, and presentation of the research results were carried out.
Results. The developed educational program for teaching patients, consisting of three stages (design, implementation, control of the educative process), and containing various methods of training, contributes to the formation of the psychological and pedagogical competence of medical workers. The specificity of the methodology is that the emphasis is on developing the ability to present information in an accessible form, and, most importantly, teach the patient and his family members specific techniques for self-monitoring, self-care and self-help.
Conclusion. The study proved the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm for teaching patients by medical workers, which was confirmed by the development of patients’ skills and abilities in selfmonitoring and self-help. Patients' behavioral habits have changed, their motivation to improve their health has increased, and they have become responsible for their health.
Aim. To identify personal characteristics determining the subject’s destructive behavior.
Material and methods. Students from Stavropol State Medical University and North-Caucasus Federal University (n=609) took part in the study. The following diagnostic methods were used: a tendency to abnormal behavior (A. N. Orel), a meaning-life orientation test (D. A. Leontyev), a self-attitude test (S. R. Panteleev), a self-organization of activity questionnaire (E. Yu. Mandrikova).
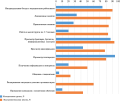
Results. We established that the sample corresponds to the characteristics of age-psychological and socio-professional development. The greatest severity by type of deviant behavior was found among respondents who are prone to overcoming norms and rules, and among those who have a reduced tendency to control emotional reactions. The least pronounced were tendencies to delinquent and addictive behavior, the tendency to aggression and violence. The dominant trends in this context are students’ understanding of the emotional richness of their ives, and the average psychological portrait of the respondent reflects their focus on themselves when implementing life’s tasks. On average, students are open to change, accept and value themselves, focus on their own strengths when planning and implementing future activities. They are focused on the present, understand the need to define the goals in life and activity. The study of individual parameters of personal characteristics and the severity of destructive behavior types made it possible to describe models of the relationship between these phenomena.
Conclusion. The study showed that the current situation in the development of society is accompanied by risk factors that cause states of emotional stress and maladaptation, which has a negative impact on mental health and behavior. Diagnosis of personal characteristics and the severity of destructive behavior types in students made it possible to describe models of the relationship between these phenomena through regression analysis. A reflexive analysis of the results obtained made it possible to reveal an invariant part of personal characteristics in models of destructive behavior and the presence of certain personal characteristics that can manifest themselves in the variable part of a model of destructive behavior.
DIGITAL EDUCATIONAL ENVIRONMENT
Aim. To determine prerequisites, content and strategic methods for implementing the author’s video-ecological approach to the infographics use in education.
Material and methods. The subject of the study was the video-ecological approach as a pedagogical system that determines the features of infographics in education. The theoretical methods involved in content creation of the video-ecological approach were the following methods: idealization, abstraction, deduction, extrapolation. The following empirical research methods were also used: sample observation, experimental conversation, questionnaire. The methods are in demand in the context of correlating digitalization and ecologization as modern trends in educational process.
Results. The video-ecological approach to the infographics use in education is presented taking into account other approaches that have become widespread at the present stage: research, narrative, competence-based, functional-activity, psychodidactic. The article contains the definition and characteristics of the structural and content filling of the epistemic spaces of video-ecological approach. Particular importance is attached to the study of prerequisites for the development of a video-ecological approach. Ecological principles of visual worldview are extrapolated into strategic techniques for implementing the videoecological approach in educational practice: interpretation of infographics, data visualization, critical analysis and creation of infographics.
Conclusion. The video-ecological approach is considered by the authors as an effective theoretical and methodological basis for the infographics use in education. The results are of interest to the scientific and pedagogical community, teachers, administrative workers of educational organizations, pedagogical students.
EVIDENCE-BASED PEDAGOGY
The outcomes of competency-based medical education (CBME), is becoming increasingly important, especially for general practitioners (GPs). The research team of the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine, with the support of the Russian Society for the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases, initiated a study "Management of the quality of training of general practitioners (family doctors)", the aim of which is to determine the priority competencies of GPs (family doctors) of the Russian Federation. As the main research approach in the ascertaining experiment, the Delphi method is proposed to use. The respondents are GPs with experience in practical healthcare, general practice residents, teachers of departments of general practice.
Conclusion. The planned research is of high significance for the theory and practice of professional education, in particular the training of GPs. Scientific rationale of GP qualification characteristics, which are the target component of the educational system for training GPs, will make it possible to determine the patterns of the educational process and the principles for selecting the content of educational programs, as well as methodological systems and conditions for training GPs. Ranking competencies according to their importance in professional activities by GPs (family doctors) of the Russian Federation will help determine key competencies and will make it possible to see the position of doctors in the priority of GP activities, which is directly related to assessing the healthcare quality
SCIENTIFIC AND PEDAGOGICAL SCHOOLS OF MEDICINE
On October 5, 2023, on the initiative of the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine and with the support of the Russian Society for the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases, the III International Research and Practice Forum "Scientific and Pedagogical Schools of Therapy and Preventive Medicine" was held. The Forum included two areas: symposiums dedicated to the best practices of higher education institutions; round tables dedicated to problems of education and practice integration.
Scientific and pedagogical schools of the Far Eastern State Medical University, Siberian State Medical University, Samara State Medical University, Northern State Medical University, Smolensk State Medical University, S. I. Georgievsky Medical Institute of the V. I. Vernadsky Crimean Federal University were represented. Scientists and practicing doctors representing the following educational organizations took part in the discussion of integration of medical education and practical healthcare: Belgorod National Research University, Kemerovo State Medical University, Medical Institute of the Derzhavin Tambov State University, V. F. Voino-Yasenetsky Krasnoyarsk State Medical University, Academy of Postgraduate Education of the Federal Scientific and Clinical Center, Research Medical Center "Gerontology", Multifunctional Medical Center (Tashkent, Republic of Uzbekistan), Ulaanbaatar Songo Hospital (Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia), First Pavlov State Medical University of St. Petersburg, Yaroslavl State Medical University, Volgograd State Medical University, Volgograd Regional Clinical Hospital № 3, National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine of the Russian Ministry of Health. The Forum showed that many medical higher educational institutions of the country have formed both independent scientific and pedagogical schools of fundamental biomedical sciences, therapy, preventive medicine, which have national and international recognition, and those that are intensively developing in accordance with Russian and international principles and demands of practical healthcare. The presence in medical education of authoritative scientific and pedagogical schools of therapy and preventive medicine is one of the indicators of the effectiveness of universities and academies in training internists and general practitioners.
The article discusses the question of identifying ageism patterns among medical students, where it is contrasted with soft skills, especially in jobs involving human-human collaborations. Modern medical students are representatives of the generation Z. This generation will determine the trends in the development of society and healthcare, in particular, for the coming decades. Understanding these trends will make it possible to specifically manage soft skills, make adjustments to medical curricula, enhancing their competitive ability to face the global labor market.
Aim. To analyze the experience of developing and testing a targeted program for improving the age-related vitality and quality of life of people in older age groups through the development of intergenerational connections, which consists of involving younger schoolchildren and their parents in voluntary work, increasing the knowledge of younger schoolchildren in aging and old age and reducing the ageism of older people.
Material and methods. This prospective cohort study consisted of 3 stages. For the study, original questionnaires were used to assess the knowledge in the field of aging processes and determine the degree of ageism among people of different ages. The study involved 138 respondents — primary school students, parents of schoolchildren, and teachers.
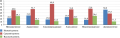
Results. The Project "Gerontological Education of Grade Schoolers" was developed and implemented, which included separate blocks. Spending time together benefits the level of good manners among grade schoolers as follows: the high level of good manners increased by 30,6%, while the average and low levels decreased by 13,9% and 66,7%, respectively. The interpretation of 4-year survey data (2019-2023) indicate that the developed system was successfully tested.
Conclusion. For the first time, a targeted program has been developed for older age groups through the development of intergenerational connections, which consists of involving grade schoolers and their parents in volunteer activities.
CURRENT EVENTS
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)