BEST PRACTICES
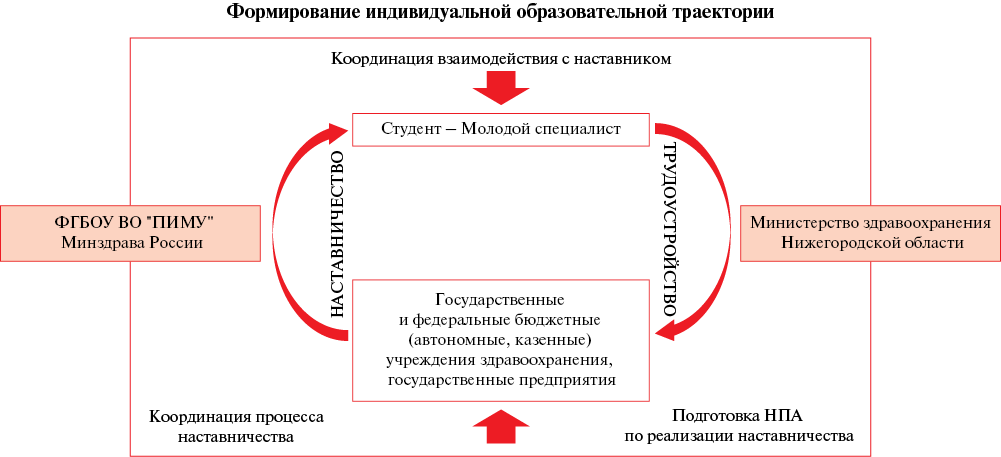
Retaining healthcare personnel through the implementation of medical mentoring aimed at adapting future healthcare professionals during training at a medical school, the development of professional involvement and competencies was the main task for the team of the Privolzhsky Research Medical University. The Medical Mentoring project was developed and is being implemented jointly with the Ministry of Health of the Nizhny Novgorod Oblast. The implementation of the project is aimed at increasing the professional adaptation of medical students and retaining medical personnel in the regional healthcare system, implementing a mentoring program in medical and pharmaceutical facilities in the doctor-mentor — student format. In addition, the integration of medical mentoring system made it possible to improve professional competencies affecting the achievement of indicators necessary for working activities. The project allows the student to adapt to the future team, feel their importance, and also develop not only professional, but also supraprofessional skills, educate and teach the future doctor at point-of-care.
Aim. The article is devoted to summarizing the experience of using peer tutoring technology at the Volgograd State Medical University in organizing various areas of mentoring at the university, as well as preparing teachers to master this educational technology in the course of pedagogy and educational technologies of additional professional education at the Grigorenko Institute of Public Health.
Material and methods. Theoretical (analysis of scientific sources on the research problem, analysis of the activities of Volgograd State Medical University mentors) and empirical research methods (observation, conversation, expert assessment method) were used. Peer tutoring management was analyzed according to the mentoring areas. In adaptation mentoring, peer tutoring was considered in the work of the "School of Curators", "School of Mentors". The analysis object in academic mentoring was peer tutoring in the activities of schools of excellence. In scientific mentoring, "School of Young Researchers" was discussed, while in social mentoring — Projectorium (youth socio-educational forum for social and innovative development), volunteering.
Results. Mentoring should be referred specifically to pedagogical technologies, since its distinctive feature is the integration of didactic and educational components. The characteristics of mentoring, tutoring, peer-tutoring technologies are given. Within the federal innovation platform of Volgograd State Medical University, in the process of implementing the innovative educational project "System of Personalized Training in a Higher Educational Institution", a review of peer tutoring practices in adaptation, scientific, academic, and social areas was conducted. Peer tutoring technology in extracurricular educational work has its own characteristics in each direction and general advantages, which contributes to students’ self-determination and inclusion in personal and professional development faster than traditional methods.
Conclusion. A variety of approaches to mentoring allows students to understand the advantage of this format of mastering novel professional and social skills in the process of extracurricular activities and, if desired, allows students to develop the mentor qualities. Mentoring and its form as peer tutoring in the student-to-professional format implements continuity and helps prepare graduates for cooperation with colleagues in a healthcare organization.
PEDAGOGY OF DEVELOPMENT AND COOPERATION
Aim. To determine the motivational component of the teacher’s psychological and pedagogical potential, as well as the differences between potential and real psychological profile and professional activity of the individual.
Material and methods. To study motivation, a questionnaire was used. In addition to the quantitative data necessary for the evidence base, qualitative processing was carried out — each answer was considered separately. The quantification analysis of social motives at the stage of diagnosis and development of their psychological and pedagogical potential served as the basis for discussing the results.
Results. The results show that before the start of the experiment, the mean values of the motive for helping people in the experimental and control groups of subjects were almost the same. After the end, the strength of this motive increased in both groups. However, in the control group the differences before and after the experiment were insignificant. In the experimental group there were more noticeable significant changes: t=2,10; p≲0,05. This means that the development of psychological and pedagogical potential among students who will become primary school teachers in the future had a positive effect on the strength of their motive for helping people. The positive results are justified by certain work that the teachers carried out with the experimental group subjects according to the program compiled by the author. The results were especially influenced by the fact that group forms of work were used during the experiment. In addition, work was carried out with students aimed at developing their affiliation motive, which is positively related to the motive of helping people. Strengthening the motive may also be associated with the acquisition of positive experiences in teaching and raising children during teaching practice, which contributes to motivation to help others.
Conclusion. The developed model of the psychological and pedagogical potential of the future primary school teacher includes structural components and areas of development. Capacity building is successful with timely diagnosis of development levels and changes in the education content. The developed diagnostic practice and capacity building concept are effective.
Aim. To analyze characteristic features of various role models of interaction between mentors and a young teacher.
Material and methods. During the research process, the analysis method was used in accordance with the following criteria: goal setting, individual character, plan for the gradual inclusion of young teachers in teaching, methodological, research and educational activities.
Results. In the study process, the following role models of interaction between mentors and a young teacher were identified: mentormethodologist — young teacher model; mentor-subject teacher — young teacher; flash mentoring model. The result of proper management of mentors is a high level of involvement of young and new specialists in pedagogical work, methodological, educational work of a young specialist, as well as in the cultural life of an educational organization.
Conclusion. We revealed that the introduction of an individual mentoring approach for young teachers helps ensure not only an increase in the personal achievements of a young specialist, but also their inclusion in teaching activities, the social life of an educational organization, increased self-confidence, the development of self-realization and adaptation to the profession. This methodology allows not only to prepare a teacher for his main job, but also to implement him as a fullfledged participant in the Federal project "Young Professionals".
NEWS FROM THE MEETING OF STATE DEPARTMENTS OF THERAPY
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)