ADDRESS TO THE READERS
ARTERIAL HYPERTENSION
What is already known about the subject?
- Machine learning methods have proven effectiveness in developing predictive tools for determining outcomes of various multifactorial diseases.
- Predicting the progression of hypertension, along with non-elective hospitalization risk for patients with this condition, and implementing timely interventions in their management are crucial for the healthcare system as a whole and for preventing complications in individual patients.
What might this study add?
- A data set was formed, including records of more than 150 thousand patients with hypertension.
- Using generally accepted technologies, based on various machine learning algorithms, a number of predictive models were developed to predict non-elective hospitalizations of these patients.
- The XGBoost-based model showed the best accuracy metrics and stability on external data.
Aim. To develop models for predicting hospitalizations of hypertensive (HTN) over 12 months using machine learning algorithms and to validate them using real-world practice data.
Material and methods. Based on the data from depersonalized electronic health records obtained from the Webiomed platform, 1165770 records of 151492 patients with HTN were selected. After the initial selection, a total of 43 anamnestic, constitutional, clinical, and paraclinical features were used as predictors. Automatic machine learning tools were used to create the models. A wide range of algorithms was considered, including logistic regression, decision tree-based methods using gradient boosting and bagging, discriminant analysis, a neural network algorithm and a naive Bayes classifier. Data from a single region were used for external validation.
Results. The XGBoost model showed the best results, achieving an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0,849 (95% confidence interval: 0,825-0,873) during internal testing and 0,815 (95% confidence interval: 0,797-0,835) during external validation.
Conclusion. A new highly accurate model for predicting hospitalization of HTN patients based on real-world data was developed. The results of external validation of the final model showed relative resistance to new data from another region that in combination with quality metrics presents the possibility of its approval for application in clinical practice.
ISCHEMIC HEART DESEASE AND MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
What is already known about the subject?
- Leptin resistance is actively studied as one of the metabolic risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.
- A relationship between visceral adipose tissue and leptin resistance is reported.
- Radiomics analysis is a new data processing method allowing extracting textural information about fat depots from tomographic images.
What might this study add?
- Radiomics analysis of magnetic resonance images of abdominal adipose tissue allows obtaining data on its composition and texture.
- The following significant factors associated with leptin resistance in patients with stable coronary artery disease were identified: Entropy, determined by magnetic resonance imaging, older age, high glucose levels, smoking and low soluble leptin receptor levels.
Aim. To evaluate quantitative and radiomic characteristics of abdominal visceral adipose tissue (VAT) using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), their relationship with lipid, carbohydrate metabolism, inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD), as well as the association of these factors with leptin resistance (LR).
Material and methods. The study included 46 patients with stable CAD. MRI was performed to determine the volume (cm3) of abdominal adipose tissue. The serum levels of glucose and insulin, lipid profile, proinflammatory markers and adipokines were determined. For quantitative assessment of LR, the free leptin index (FLI) was calculated (FLI >25 indicates LR).
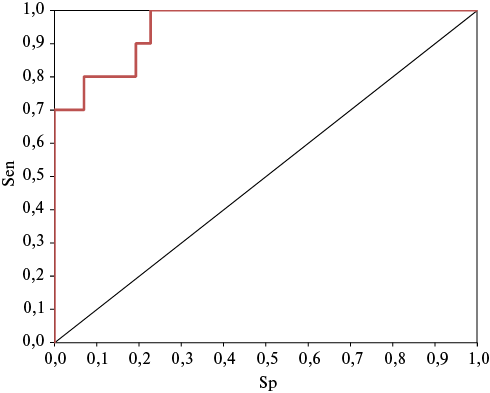
Results. In the group with LR, body mass index and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), the levels of insulin, adiponectin, leptin and FLI were significantly higher, while the adiponectin/leptin ratio and the blood level of leptin receptors were lower than in the group of patients without LR. No intergroup differences in abdominal fat volume were found. The group with LR was characterized by a significantly lower value of such radiomic characteristics as Entropy and Variance. The following factors associated with LR were included in the multivariate logistic regression analysis model: age (odds ratio (OR) 1,24, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1,05-1,47), glucose level (OR 2,50, 95% CI: 0,73-8,62), soluble leptin receptor level (OR 0,65, 95% CI: 0,47-0,91), smoking (OR 0,43, 95% CI: 0,065-2,89) and Entropy (OR 2,44, 95% CI: 0,13-46,5). The sensitivity and specificity of the model are 90,6 and 57,1%, respectively.
Conclusion. Significant factors associated with LR in patients with stable CAD were identified: Entropy, older age, high glucose levels, smoking, and low levels of soluble leptin receptors.
What is already known about the subject?
- The main mechanism of thanatogenesis of sudden cardiac death is life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias.
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT) in patients with myocardial infarction (MI) is transient, so it is not always possible to record it.
What might this study add?
- The main factors associated with the risk of nonsustained VT in patients with MI were identified.
- A comprehensive multifactorial model for predicting the nonsustained VT in patients with MI at the hospital stage was proposed.
Aim. To identify markers of ventricular tachycardia (VT), as well as to create a multifactorial prediction model for arrhythmic events in inpatients with myocardial infarction (MI).
Material and methods. The study included 80 patients with MI aged 55,6±8,7 years. The following examination was carried out on days 7-9 of MI: echocardiography, assessment of global longitudinal strain (GLS), contrast-enhanced cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), determination of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). During 72-hour electrocardiographic (ECG) monitoring, we detected VT runs, as well as analyzed microvolt T-wave alternans (TWA), heart rate turbulence, late ventricular potentials, heart rate variability, cardiac chronotropic load, and QT dispersion. The end point was the presence of ≥1 VT episode (≥3 QRS complexes) according to multi-day ECG monitoring data.
Results. Nonsustained VT runs were recorded in 10 (12,5%) patients, who made up the VT group. The remaining 70 (87,5%) people who did not have VT episodes were included in the comparison group. MRI data established that the scar tissue mass (36,8±23,7 g) and percentage (28,5±19,8%) in the VT group was higher than in the comparison group (16,9 (6,5; 27,9) g (p=0,025) and 13,3 (5,8; 22,2)% (p=0,045), respectively).
Univariate regression analysis revealed following factors associated with the VT risk: history of coronary artery disease, high NT-proBNP values, heart rate turbulence, microvolt TWA, end diastolic dimension, GLS, scar tissue mass, scar area from total myocardial mass (%), night-time heart rate variability parameters — ULfP, TINN, SDANN.
Conclusion. A multifactorial model for predicting non-sustained VT in patients with MI is proposed, including the following parameters: end-diastolic dimension, MAT, NT-proBNP, GLS, scar tissue mass, and history of coronary artery disease.
HEART FAILURE
What is already known about the subject?
- Initiation of dapagliflozin early in the course of an acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) hospitalization among patients with diabetes may facilitate both decongestion and optimization of chronic heart failure (HF) medical therapies. The study shows that dapagliflozin reduces HF in broad spectrum of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients admitted with ADHF.
What might this study add?
- This study concluded a significant reduction in body weight, dyspnea scale, and increase in the SpO2at 4thday of admission of intravenous (iv) Furosemide plus dapagliflozin and iv Furosemide only.
- This study showed the effectiveness of drugs on reduction of N-terminal fragment of brain natriuretic propeptide (NT-proBNP) level at 4thday of admission.
- The study demonstrated increase urea and creatinine levels at 4thday of admission.
Aim. HF is a complex clinical syndrome that manifests with symptoms such as dyspnea (shortness of breath) and fatigue. It can arise from various conditions that impact ventricular filling (diastolic dysfunction) or myocardial contractility (systolic dysfunction). Additionally, clinical signs like pulmonary rales, peripheral edema, or distended jugular veins may be present. The aim of the present study was to observe the possible effect of dapagliflozin on serum NT-proBNP level in ADHF and its relationship with weight.
Material and methods. Between October 2023 and April 2024, a study was conducted at AL-Nassiriyah Heart Center, in the coronary care unit (CCU), in Thi-Qar city southern of Iraq. One hundred subjects both males and females were enrolled in study after describing the study's goals, gauging patient satisfaction, and getting informed consent from the subjects. 100 enrolled patients were divided into two groups: Control group (Group A) involved (50 patients), given intravenous (iv) furosemide (120 mg/day) and Studied group (Group B) involved (50 patients), given iv furosemide (120 mg/day) plus 10 mg dapagliflozin tablet daily.
Results. It was found a significant reduction in body weight and BMI of patients during 4th day of hospital admission compared with days of admission in both groups (A&B). However, body weight and BMI of group B patients during 4th day of hospital admission were significantly lower compared to 4th day of admission in group A. Serum NT-proBNP during 4th day of admission in group B patients during 4th day of admission were significantly lower compared to group A patients during 4th day of admission. It was found that dapagliflozin, compared with control, reduced NT-proBNP levels in patients with HFrEF.
Conclusion. Dapagliflozin reduced the risk of worsening HF events and cardiovascular death, and improved symptoms, across the spectrum of baseline NT-proBNP levels. Also, it was confirmed the strong association between higher NT-proBNP levels and worse outcomes in HFrEF. Because body weight and NT-proBNP were decreased at 4th day of drug treatment, fluid loss must have been induced at the same time. The present study has reported a positive effect of dapagliflozin to reduce level of NT-proBNP and weight in patient with ADHF.
What is already known about the subject?
- Free nucleotides in blood plasma are universal indicators of the impact of a stress factor.
- Changes in the metabolism of free nucleotides are associated with the adaptive needs of the body under the damaging effects of stress agents.
What might this study add?
- A reliable difference in the levels of free nucleotides in patients with heart failure compared to the control group was revealed, which may be due to the peculiarities of cellular metabolism under hypoxia.
- Levels of free nucleotides are subject to changes over treatment, which is confirmed by the example of patients with a reduced ejection fraction.
Aim. To assess the potential of studying the plasma level of free nucleotides as additional biomarkers of heart failure (HF) taking into account the clinical and paraclinical data of the patient, and to analyze its change during therapy.
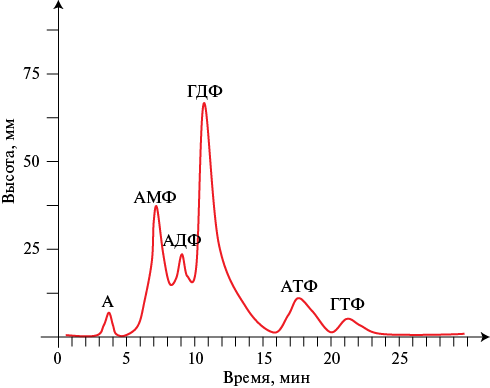
Material and methods. The study included 67 patients with HF and 23 healthy volunteers. The plasma content of free nucleotides was analyzed by chromatography on an automated FPLS® System (Sweden), 10 × 200 mm column with Q Sepharose Fast Flow. Repeated analysis was performed in patients with a reduced ejection fraction after 6±0,2 months.
Results. In patients with HF, compared with the control group, we found lower levels of adenosine — 30,45±2,61 vs 56,68±3,99 mm2 (p=0,001), adenosine monophosphate — 278,60±18,60 vs 391,68±39,86 mm2 (p=0,022), guanosine diphosphate — 500,27±22,83 vs 901,63±51,09 mm2 (p=0,001), adenosine triphosphate — 49,25±8,89 vs 145,18±18,80 mm2 (p=0,001), guanosine triphosphate — 32±8,25 vs 92,40±27,07 mm2 (p=0,041) and higher adenosine diphosphate values — 690,10±57,41 vs 392,09±32,63 mm2 (p=0,002). These patterns were preserved when analyzing taking into account the ejection fraction, functional class and the presence of diabetes. During treatment, the levels of adenosine diphosphate and guanosine diphosphate significantly change (up to 307±26,08 mm2 and 650,47±58,1 mm2, respectively), approaching the values in the control group.
Conclusion. The revealed features of the nucleotide profile in HF make it possible to consider the level of free nucleotides as an additional potential biomarker reflecting objective disorders at the cellular level.
КАРДИООНКОЛОГИЯ
What is already known about the subject?
- The use of anthracycline antibiotics for the treatment of cancer, including oncohematological diseases, is often the cause of cardio-oncological complications, leading to death both during chemotherapy and in the long-term period.
- Modern multicenter studies have shown higher concentrations of galectin-3 and interleukin (IL)-6 biomarkers in patients with proven cardiac diseases, demonstrating the role of remodeling processes and systemic inflammation in the development of cardiovascular pathology.
What might this study add?
- In patients with proven lymphomas, before chemotherapy, the levels of galectin-3 and IL-6 are significantly higher than in patients with similar cardiovascular status without a history of oncopathology.
- In patients with lymphoproliferative disease, the role of galectin-3 and IL-6 is difficult to assess due to disease pathogenetic features.
Aim. To study the significance of proinflammatory markers, galectin-3 levels, lipid profile parameters, cardiovascular status and their relationship in patients with lymphomas before the start of specific antitumor therapy, as well as to compare the studied parameters with patients with similar cardiovascular status without cancer.
Material and methods. The study included 2 following groups of patients: the main group (n=30) — patients with newly diagnosed lymphoproliferative disease (LPD), the comparison group (n=30) — patients with similar risk factors and/or proven cardiovascular pathology and without cancer. All patients included in the study underwent determination of inflammation markers, lipid profile and special markers (concentration of interleukin-6 (IL-6) and galectin-3).
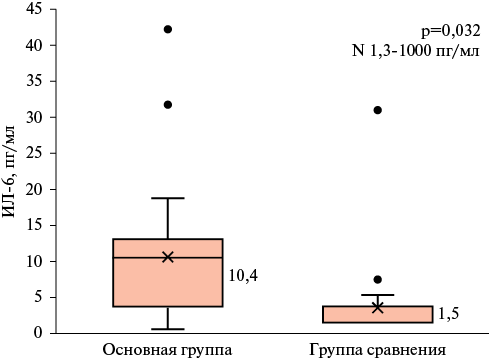
Results. The patients of both groups included in the study were comparable in age, sex, risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, cardiovascular therapy. In patients of the main group, the level of potentially proatherogenic lipids in the group of patients with lymphomas was slightly higher than in the comparison group, although the differences did not reach statistical significance (p>0,05); the levels of acute phase proteins (C-reactive protein, ferritin, fibrinogen), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (p<0,05 for all parameters), IL-6 (p=0,032), galectin-3 (p=0,001) were significantly higher. Intragroup analysis in the LPD group using International Prognostic Index (IPI), Mantle cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI) and Follicular Lymphoma International Prognostic Index depending (FLIPI) demonstrated that the levels of galectin-3 and IL-6 were higher in patients with the worst prognosis indices. The correlation analysis revealed a direct moderate relationship between galectin-3 and IL-6 (r=0,488; p=0,016).
Conclusion. The study showed that the study groups did not differ significantly in terms of the level of potentially proatherogenic lipids. The results of the comparative analysis demonstrate that the concentration of galectin-3 and IL-6 in LPD is significantly higher than in the comparison group; their high level may reflect the activity of the tumor process. The significance of these biomarkers in the development of cardiovascular toxicity complications in patients with LPD has not yet been studied and seems interesting from the point of view of their possible predictive role for cardiovascular complications of chemotherapy.
RESEARCH METHODS
What is already known about the subject?
- Stepwise stratification of cardiovascular risk using the SCORE 2 scale is currently recommended in relatively healthy individuals.
- Cardiovascular events were registered in population samples of the Russian adult population as part of the ESSE-RF epidemiological study.
What might this study add?
- The majority of cardiovascular events occur in individuals with high and very high risk according to clinical and anamnestic data and the results of carotid ultrasound.
- The SCORE2 scale defines high and very high risk in 98% of relatively healthy individuals, which raises questions about the appropriateness and effectiveness of its use in the Russian Federation.
Aim. To study the effectiveness of cardiovascular risk (CVR) stratification using the systematic coronary risk evaluation 2 (SCORE2) in a Tomsk adult population sample based on 5-year follow-up.
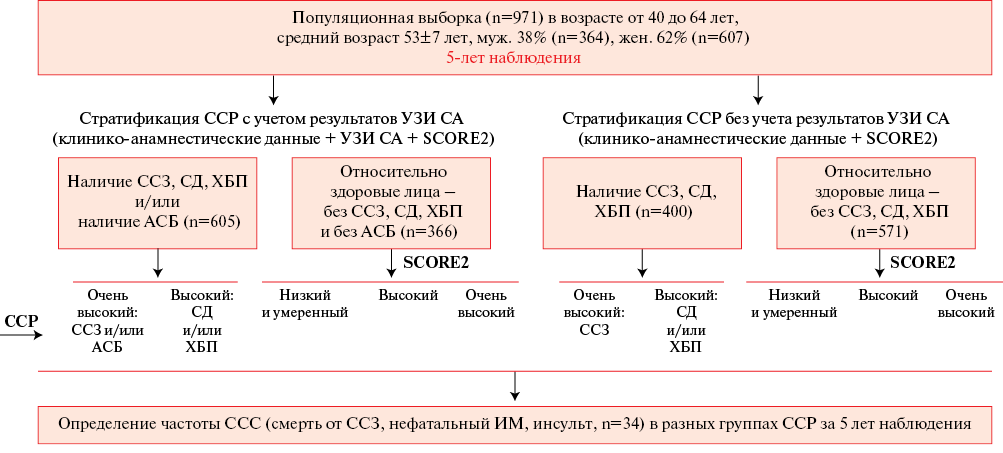
Material and methods. The results of a survey of a population sample of 971 people aged 40 to 64 years in Tomsk were analyzed as part of the ESSE-RF study. Based on clinical and anamnestic data on atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (with and without taking into account carotid ultrasound data), as well as diabetes or chronic kidney disease (CKD), individuals with high and very high risk were identified. CVR in relatively healthy individuals was assessed using the SCORE2 scale. The incidence of cardiovascular events (CVEs) (cardiovascular death, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke (n=34)) were determined in different risk groups based on 5-year follow-up.
Results. Coronary artery disease was registered in 140 examined persons (15%), type 2 diabetes in 137 people (14%), CKD in 217 (22%), history of MI or stroke in 5,3%. The category of high and very high CVR according to clinical and anamnestic data included 400 examined persons (41%), which accounted for 22 out of 34 (65%) CVEs over the 5-year follow-up period. The use of the plaque presence criterion identified in 386 subjects (40%) expanded this group to 605 subjects (62%), who accounted for 30 out of 34 (88%) CVEs during the follow-up period (5%), which significantly increased the detection of subjects with CVEs (p=0,04). According to the SCORE2 scale, 98% of 366 relatively healthy subjects were at high and very high risk, but CVE incidence during the follow-up period was only 1% (p=0,004).
Conclusion. The results of the 5-year follow-up demonstrated the effectiveness of the modern CVR stratification algorithm in a population sample of Tomsk aged 40 to 64 years in identifying subjects with high and very high risk based on clinical and anamnestic data, taking into account carotid ultrasound data, who account for the majority (88%) of CVEs (cardiovascular death, non-fatal MI, stroke). The SCORE2 scale identified high and very high risk in 98% of relatively healthy individuals, while the incidence of CVEs in them was only 1% over 5-year follow-up, which does not confirm the effectiveness and feasibility of SCORE2 scale in CVR stratification.
OPINION ON A PROBLEM
What is already known about the subject?
- In real-world practice, oral/sublingual medications are often used to quickly reduce asymptomatic/low-symptom elevated blood pressure (BP), although such management of uncomplicated hypertensive crises is not supported by modern guidelines.
What might this study add?
- Based on research data, criticism of such rapid "treatment" of hypertension is substantiated, which does not bring benefits, but can increase the risk of cardiovascular events.
- Rational actions of a physician when detecting asymptomatic/low-symptom BP increase, possible approaches to home self-monitoring of BP, as well as management of true hypertensive crises are described.
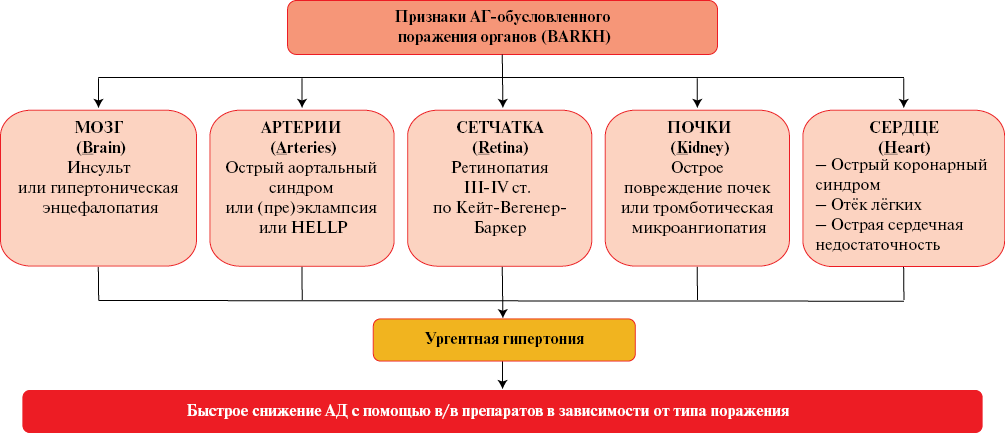
Contrary to modern guidelines for the treatment of hypertension, oral and sublingual antihypertensive medications are often used in real-world practice to quickly reduce asymptomatic or low-symptom elevated blood pressure (BP). Doctors and patients explain this by the need to "stop an uncomplicated hypertensive crisis" for preventing cardiovascular events. Clinical trial data indicate that such an approach, both the prescription of short-acting drugs at an outpatient or inpatient levels, and recommendations for self-treatment of hypertension, not only does not benefit the patient, but is also likely to be associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular events. Shifting the focus of hypertension treatment from improving the long-term prognosis to immediate BP reduction may increase short-term variability of BP, which is a possible mechanism for the development of complications when using fast-acting oral antihypertensives. The article substantiates the unacceptability of emergency BP reduction with oral and sublingual antihypertensive drugs. It describes rational actions of a physician in case of detection of asymptomatic or low-symptom BP increase in a patient and presents possible approaches to home BP self-monitoring in accordance with modern clinical guidelines. It also describes the management of true hypertensive crises depending on the characteristics of hypertension-mediated organ damage.
OPINION OF INVITED EDITOR
CLINICAL CASE
- A case of constrictive pericarditis is described, the features of which are the etiology — vaccination or infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), torpidity of pericarditis course, especially in the elderly — without severe fever and chest pain, hemodynamic constrictive disorders, without severe thickening and calcification of the pericardium, and as a consequence — late diagnosis and prescription of adequate anti-inflammatory treatment.
- Despite the pericardiectomy, after 2 months there was no regression of heart failure, while inflammatory markers (C-reactive protein and antinuclear factor) remain elevated.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy of polyserositis with colchicine and anakinra made it possible to achieve complete heart failure compensation.
A case of a 70-year-old male patient is presented, in whom constrictive-effusive pericarditis debuted after vaccination against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and over the six months progressed in edema and ascites, refractory to therapy. A year later, after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), signs of increasing heart failure were noted, accompanied by an increase in proinflammatory markers, myocardial damage indicators. The diagnosis of constrictive-effusive pericarditis was made another 9 months later at the anasarca stage. The difficulties in diagnosis were that the pericardium remained non-thickened according to radiological methods. In addition, there were discrepancies in the data of computed tomography and echocardiography. Cardiac decortication was performed. However, within 2 months after the operation, no significant edema and ascites regression was achieved. In addition, the levels of inflammatory markers remained elevated, which was assessed as polyserositis. Anti-inflammatory therapy with anakinra and colchicine was prescribed with successful edema and ascites resolution within 2 months. The genetically engineered drug was gradually discontinued, and colchicine was continued for up to a year. During control examinations after 6, 12, and 18 months, no exacerbations were observed, and the NYHA heart failure class 1 remained. The patient receives minimal therapy, including eplerenone 25 mg, torasemide 5 mg, and atorvastatin 20 mg.
Conclusion. The peculiarity of pericarditis course in this case is a rapidly progressing increase with unclear inflammatory manifestations, progression with repeated stimulation with viral antigens, rapid development of constriction without significant thickening of the pericardial leaflets. Persistent polyserositis can be the cause of therapy-resistant edema and ascites in patients after pericardiectomy. The possibility of torpid inflammation in patients with edema and ascites should be taken into account.
LITERATURE REVIEW
What is already known about the subject?
- Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) in hypertension increases the risk of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, sudden cardiac death, stroke and all-cause death.
- Regression of LVH during treatment of hypertension is associated with a favorable effect on cardiovascular prognosis.
What might this study add?
- The article presents current data on LVH regression during antihypertensive therapy, including new classes of drugs — angiotensin receptor/neprilysin inhibitors and sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), which is the main manifestation of hypertensive heart disease, is registered in 15-45% of patients with hypertension (HTN), reaching 77% in patients with resistant HTN, concomitant type 2 diabetes and a history of cardiovascular events. The presented review covers the main issues of definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology, diagnostics and regression of LVH with antihypertensive therapy. Recommendations, criteria for detection, advantages and disadvantages of electrocardiography and echocardiography in the management of patients with HTN and LVH are provided. Particular attention in the review is paid to the discussion of LVH influence on the cardiovascular prognosis and the validity of hypertrophy regression. LVH often occurs with the absence or erased clinical manifestations, but over time it increases the risk of heart failure, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, sudden cardiac death, stroke and all-cause death. Timely and adequate antihypertensive therapy allows not only to reduce blood pressure, but also to achieve regression of LVH, which has a favorable effect on the outcome. The main groups of pharmacotherapy causing LVH regression are presented, among which renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, including in combination with a neprilysin inhibitor), β-blockers, calcium channel blockers, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and diuretics are discussed in detail.
ЭПИДЕМИОЛОГИЯ И ПРОФИЛАКТИКА СЕРДЕЧНО-СОСУДИСТЫХ ЗАБОЛЕВАНИЙ
What is already known about the subject?
- Smoking is a risk factor for known respiratory and cardiovascular diseases complicating coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), and, therefore, a potential risk factor for the development of COVID-19 and its complications.
- Data on the relationship between smoking and the incidence of COVID-19 and its outcomes are contradictory.
What might this study add?
- The article presents the results of the analysis of national and regional trends, features of the relationship between smoking and COVID-19 outcomes by age and sex groups of the adult population.
- The relationship between the smoking rate and severe COVID-19 and related mortality demonstrates a non-linear direction, significantly variable depending on age.
- The obtained results provide opportunities for additional research aimed at an in-depth study of the causal relationships between smoking and COVID-19 outcomes.
Aim. To study the relationship between the level of hospitalizations, severe course, and mortality from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) with the smoking prevalence in Russia for 2020-2021.
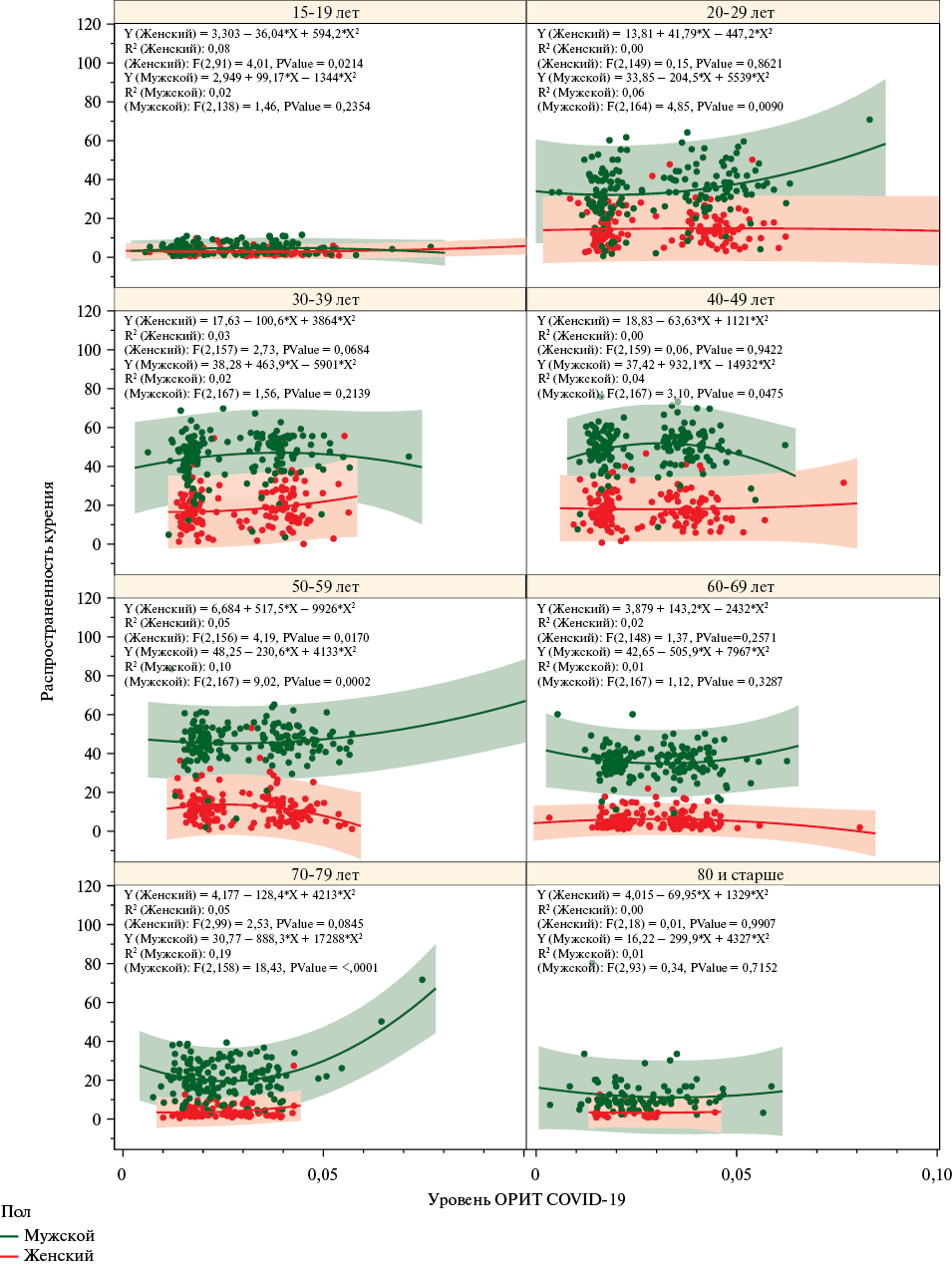
Material and methods. The article analyzes data on the number of people hospitalized with COVID-19, transferred to the intensive care unit (ICU), and died from COVID-19 in 2020-2021 by age and sex groups in 85 Russian regions from the Federal COVID-19 Registry, as well as data on smoking status, socio-demographic characteristics of the sample for 2020-2021 in 85 Russian regions from the Sample Monitoring of the Population Health sample of the Federal State Statistics Service for the corresponding years. Relationships between the smoking and COVID-19 and severe COVID-19 hospitalization rates with transfer to the ICU and the COVID-19 mortality rate by age and sex groups and federal districts of Russia were analyzed. The assessment was carried out using second-order polynomial regression (quadratic regression). The model quality was determined based on the coefficient of determination (R2) and the F-criterion for the general model.
Results. Nonlinear relationships between the studied parameters with a characteristic parabolic dependence were obtained. A significant relationship was found between the prevalence of smoking and the level of severe COVID-19 among men in the age groups of 20-29 years, 50-59 years, 70-79 years (p<0,05). A relationship was found between COVID-19 mortality and smoking rate in men aged 15-19 years (R2=0,15, p=0,049), more significant in women (R2=0,35, p=0,002); in women aged 30-39 years (R2=0,06, p=0,007); in men and women aged 40-49 years and 50-59 with a more pronounced trend; in men aged 60-69 (R2=0,05, p=0,018) and in women as a trend (R2=0,03, p=0,078); in women aged 70-79 and ≥80 years (R2=0,06, p=0,039) with a more pronounced trend in men. Positive associations were found between smoking prevalence and the rate of hospitalization for COVID-19 (R2=0,52, p<0,001) and severe COVID-19 (p=0,011) in the Far Eastern Federal District among men, as well as in the Siberian Federal District (p=0,007) and the Ural Federal District. The relationships between the mortality rate from COVID-19 and smoking frequency in different federal districts demonstrate an inverse parabolic dependence.
Conclusion. The relationships between smoking and COVID-19 rates are complex and nonlinear. A deep segmented analysis of these relationships revealed significant associations explaining the contribution of smoking to the rate of hospitalizations and severe outcomes, mortality from COVID-19 in certain age groups of men and women and in various federal districts of Russia. Effective tobacco control measures aimed at reducing smoking are necessary to mitigate the adverse effects of coronavirus infections.
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)