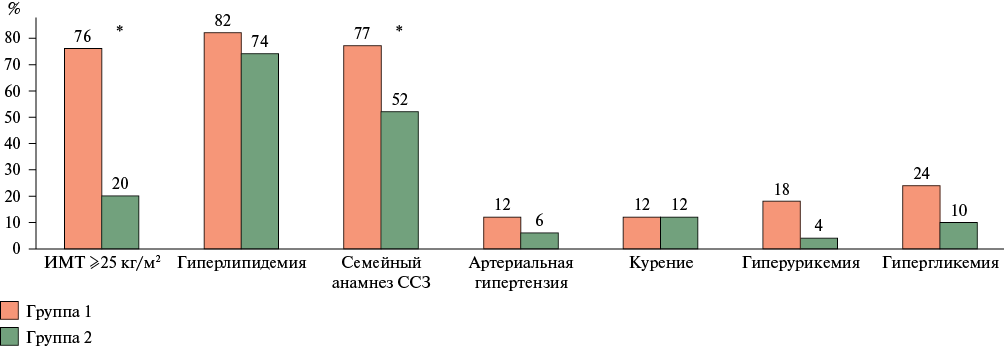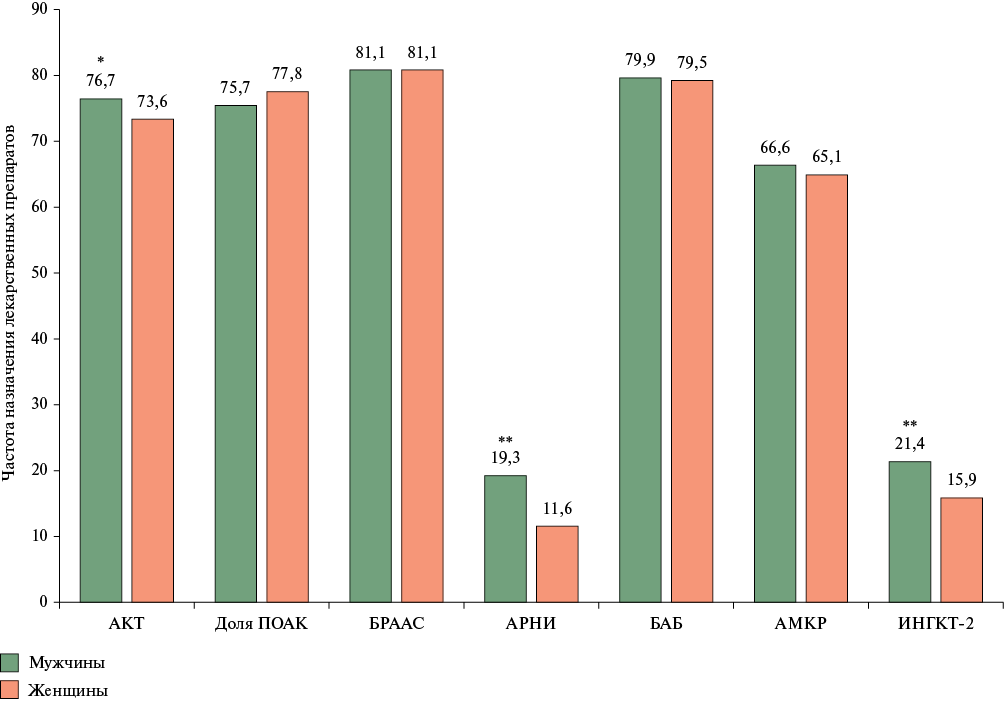ADDRESS TO THE READERS
ДИСЛИПИДЕМИИ И ИШЕМИЧЕСКАЯ БОЛЕЗНЬ СЕРДЦА
What is already known about the subject?
- Adipose tissue can release a large number of proinflammatory cytokines, which affects the plaque development and destabilization.
- Pericoronary fat attenuation index (FAI) is able to record the changes of perivascular fat density, allowing for the early detection of chronic inflammation areas.
What might this study add?
- FAI in patients with acute coronary syndrome is significantly associated with vulnerable plaques, lipid profile parameters, as well as markers of inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling.
Aim. To study the relationship between the pericoronary fat attenuation index (FAI), markers of inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling, and vulnerable plaque criteria according to computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA) in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Material and methods. This study, carried out within the prospective single-center clinical trial Combi-LLT (NCT05624658), included 72 patients aged 57 (50;67) years. Of these, 68,1% were men, admitted with the clinical performance of ACS. All underwent percutaneous coronary intervention of the infarct-related artery. All patients had plaques with <50% stenosis. After 1 month, we performed CTCA to detect vulnerable plaques, as well as assess FAI, lipid profile, levels of inflammation biomarkers, and extracellular matrix remodeling as follows: neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), monocyte-to-high-density lipoprotein ratio (MHR), matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1), galectin-3 (Gal-3), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). The follow-up period was 12 months.
Results. Myocardial infarction (MI) was diagnosed in 56 patients (78%), including ST-elevation MI in 33 (46%) and non-ST-elevation MI in 23 (32%), while the remaining patients had unstable angina. Vulnerable plaque criteria according to CTCA were identified in 42 patients (58%). FAI in the left anterior descending (LAD) artery with plaques with a low-density area was higher (median -76 and -98 HU, respectively, p=0,038). In the presence of punctate calcifications, FAI in the LAD was also higher (median -67 and -90 HU, respectively, p=0,045). The threshold level of FAI for the vulnerable plaque using the punctate calcification criterion was -73,5 HU (area under the curve (AUC) =0,80 (95% confidence interval: 0,587-1,0, p=0,05), sensitivity 75%, specificity 80%). The threshold level of FAI for the low-density area was -92 HU (AUC =0,73 (95% confidence interval: 0,537-0,916, p=0,038)). Sensitivity and specificity were 79 and 60%, respectively. After 12 months, there was a decrease in FAI in the LAD from -77 (-85;-72) HU to -84 (-98;-71) HU (p=0,014). However, in patients with ST-elevation MI it remained higher compared to patients with unstable angina (p=0,002). In patients with achieved target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level, FAI in the right coronary artery significantly decreased as follows: -70 (-82;-62) HU vs -78 (-90;-60) HU (p=0,022). The above-mentioned biomarkers were higher among individuals with FAI≥-70,1 HU compared to FAI<-70,1 HU as follows: NLR — 2,3 (2,1;3,2) and 1,9 (1,5;2,3), respectively (p=0,015); PLR — 133 (98;185,4) and 106,4 (83,3;128,9) (p=0,026), MMP-9 — 36 (25,87;44,2) and 25,9 (17,84;34,85) (p=0,026), Gal-3 — 5,65 (3,03;6,87) and 3,05 (2,03;8,68) (p=0,035).
Conclusion. FAI in patients after ACS has a significant relationship with vulnerable plaques in the non-infarct-related artery, lipid profile parameters, as well as inflammation and matrix remodeling markers. The obtained data may be useful in stratifying cardiovascular risks and identifying new targeted preventive strategies.
COVID-19 AND DISEASES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
What is already known about the subject?
- Since the end of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the incidence of cardiovascular disease and major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) has increased in patients COVID-19 survivors.
- One of the ways to diagnose cardiovascular alterations in patients with COVID-19 is to assess the following serum biomarkers: high-sensitivity troponin T and high-sensitivity troponin I, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, D-dimer, soluble tumorigenicity suppression protein (sST2) and pentraxin 3 (PTX3).
What might this study add?
- Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and without documented cardiovascular disease are at increased risk of MACE during the first year after discharge.
- To determine the probability of long-term MACE, the concentrations of PTX3, sST2 and D-dimer should be assessed.
- Defined cut-off values of cardiac biomarkers PTX3, sST2 and D-dimer may be used to stratify long-term cardiovascular risk in patients after COVID-19.
Aim. To determine the potential role of conventional and potential biomarkers in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) in the long-term period after coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Material and methods. On the day of hospitalization, 112 inpatients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 were assessed for biomarkers such as high-sensitivity troponin T (hsTnT) and troponin I (hsTnI), N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), D-dimer, soluble tumorigenicity suppression protein (sST2) and pentraxin 3 (PTX3). COVID-19 survivors were followed for a median period of 366 [365; 380] days after discharge from the COVID hospital, assessing the incidence of MACE (myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism, cerebrovascular accident, cardiovascular death).
Results. During the one-year follow-up period, the study endpoints (MACE) were registered in 14 (12,5%) patients. Of the cardiovascular biomarkers studied, differences were found in the levels of both conventional (hsTnT, D-dimer) and potential biomarkers (sST2, PT3) in the groups of patients with and without MACE. Groups did not differ significantly in NT-proBNP and hsTnI levels (p>0,05). According to multivariate analysis, the strongest predictors of MACE development are body mass index >29,5 kg/m2 (Area Under The ROC Curve (AUC) 0,672, sensitivity 45%, specificity 23,9%, p=0,001), PTX3 >3,1 ng/ml (AUC 0,885, sensitivity 94,0%, specificity 82,1%, p=0,001), sST2 >36 ng/ml (sensitivity 92,9%, specificity 33%, p=0,001), D-dimer >0,4 μg/ml (AUC 0,787, sensitivity 93%, specificity 72,4%, p=0,049). A mathematical model based on the concentration of PTX3, sST2 and D-dimer biomarkers predicts MACE within 1 year after COVID-19 with a sensitivity of 92,9%, specificity of 61% and predictive accuracy of 90,5% (p<0,001).
Conclusion. Determination of the concentration of biomarkers such as D-dimer, sST2, PT3 can be used to predict long-term MACE in patients after COVID-19.
МЕТАБОЛИЧЕСКИЕ НАРУШЕНИЯ
What is already known about the subject?
- Prediabetes is a condition characterized by carbohydrate metabolism disorders (impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance) that do not reach the diagnostic criteria for diabetes. Prediabetes is a proven risk factor not only for diabetes, but also for cardiovascular diseases, and death from them.
- The most important task in managing patients with prediabetes is to prevent the transition of this pathological condition to diabetes.
- Metformin is the only drug currently registered on the Russian pharmaceutical market with the indication of prevention of diabetes in prediabetes.
What might this study add?
- The prevalence of initial carbohydrate metabolism disorders (prediabetes) in the cohort of patients in the outpatient registry was lower than that demonstrated in epidemiological studies, which may indicate incomplete diagnosis of prediabetes in practice.
- Patients with prediabetes occupy an intermediate position in comorbidity between individuals with normal glycemia and patients with diabetes.
- Metformin therapy for prediabetes in practice is prescribed in an extremely low percentage of cases.
Aim. To study the main characteristics of a cohort of patients with initial carbohydrate metabolism disorders (impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) or prediabetes), as well as real-world metformin prescription rate according to the PROFILE outpatient registry.
Material and methods. This cross-sectional study was conducted within the PROFILE registry — an outpatient registry of the specialized cardiology department of the research center. All patients with cardiovascular diseases and related risk factors who sought consultation in this department were included. The PROFILE registry database, compiled on the basis of case report forms (CRFs), was used to determine the number of patients with an established diagnosis of IGT, the main characteristics of this cohort. We compared subgroups of patients without carbohydrate metabolism disorders and with type 2 diabetes (T2D), as well as assessed metformin prescription rate in patients with IGT.
Results. At the time of the study, 2619 people were included in the PROFILE registry, of which 1321 (50,4%) were men. According to the CRFs (initial visit), the diagnosis of IGT was established in 290 (11,1%) patients. In this cohort, there were 129 (44,5%) men, while the mean age of all patients with IGT was 61,4±12,3 years. Patients with prediabetes and diabetes were significantly more likely (p<0,05) to have obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and heart failure than patients with normal carbohydrate metabolism parameters. Drug prevention of diabetes was recommended only to 13 (4,5%) patients with IGT. In the group receiving metformin, there were significantly more patients with obesity — 84,6 vs 52,2% (p=0,022). A tendency was also found for more frequent drug prevention of diabetes in adherent patients with IGT — 84,6 vs 59,9% (p=0,074).
Conclusion. Within the outpatient registry of patients with cardiovascular diseases and related risk factors, the IGT was established in 11,1% of patients. Women predominated in this cohort. Patients with prediabetes occupied an intermediate position in comorbidity burden between individuals with normal glycemia and patients with diabetes. Metformin therapy for prediabetes in real-world practice was prescribed only in 4,5% of cases.
#Working group of the PROFILE registry: Budaeva I. V., Voronina V. P., Dmitrieva N. A., Drapkina O. M., Zagrebelny A. V., Kutishenko N. P., Lerman O. V., Lukina Yu. V., Martsevich S. Yu., Nekoshnova E. S., Tolpygina S. N., Shepel R. N.
What is already known about the subject?
- Cardiometabolic factors are associated with the risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and cardiovascular diseases.
- Assessment of visceral fat content using bioelectrical impedance represents a cost-effective and widely available alternative to magnetic resonance imaging in quantifying total adipose tissue.
What might this study add?
- Young adults with NAFLD have a higher prevalence of overweight/obesity, positive family history of cardiovascular disease, hyperuricemia, and hyperglycemia, along with higher serum triglyceride levels and lower serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels compared to individuals without NAFLD.
- When assessing body composition, young adults with NAFLD have higher total and visceral fat levels compared to individuals without NAFLD.
Aim. To compare cardiometabolic risk factors, metabolic parameters and body composition in young adults with and withou tnon-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Material and methods. This observational case-control study included 100 participants, which were divided into groups 1 (n=50) and 2 (n=50) with and without NAFLD, respectively. The mean age in the NAFLD group was 38 [34-40] years, while in the group without NAFLD — 34,5 [28-38] years (p=0,004). Clinical and paraclinical examination was conducted. Body composition was determined using bioelectrical impedance analysis on Inbody 370 analyzer.
Results. Young adults with NAFLD had a higher prevalence of overweight/obesity, positive family history of cardiovascular disease, hyperuricemia, and hyperglycemia, along with higher serum triglyceride levels and lower serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels compared to individuals without NAFLD. Body composition assessment showed that young adults with NAFLD had higher total and visceral fat levels compared to individuals without NAFLD. Visceral fat levels in young adults with NAFLD were positively associated with anthropometric (waist circumference, body mass index, waist/hip ratio) and metabolic (fasting insulin) parameters.
Conclusion. Identification of a cluster of cardiometabolic risk factors in young individuals with NAFLD is important in clinical practice for early intervention, which can significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases and complications. Visceral fat accumulation is closely associated with NAFLD and hepatic steatosis, which determines the importance of assessing body composition with visceral fat measurement in such patients.
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
What is already known about the subject?
- Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a reliable risk factor for cognitive impairment.
- Long-term AF leads to cerebral atrophy according to magnetic resonance imaging and to a decrease in cerebral blood flow (inflow), studied by scintigraphy and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Ultrasound data on cerebral venous outflow in AF are rare.
What might this study add?
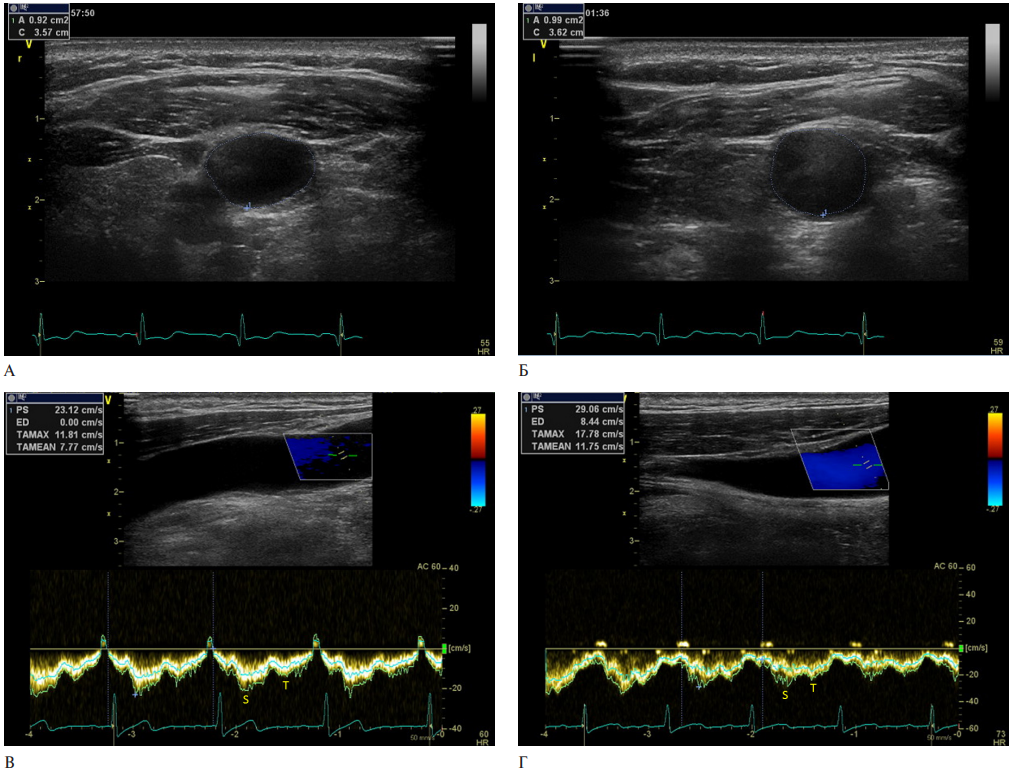
- Patients with AF are characterized by dilated internal jugular veins and decreased velocity parameters (time-averaged maximum and mean velocities, S, T peak velocities) to the lower reference limit.
- Ultrasound of internal jugular veins in patients with AF reflect the initial signs of venous outflow impairment.
Aim. To study changes of geometric and hemodynamic characteristics of internal jugular veins (IJVs) using ultrasound in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). Today, we have quite a lot of data on changes in cerebral arteries. There is much less information about venous changes using such a simple and accessible method as ultrasound, and data on cerebral venous outflow in AF are insufficient.
Material and methods. This observational study included patients with permanent AF and patients with sinus rhythm and no history of arrhythmias. The AF group included 29 patients with AF, while the control group — 41 patients without arrhythmias. All patients underwent ultrasound of the following vessels: extracranial — IJV and common carotid artery (CCA), intracranial — basal vein of Rosenthal and middle cerebral artery. Arterial pressure and venous pressure (VP) in the brachial vein were measured.
Results. According to the clinical characteristics of VP and central VP, patients in the AF group and the control group did not differ significantly. The area of the IJV was larger in the AF group as follows: on the right — 2,1±0,66 and 1,32±0,35 cm2 in the AF group and in the control group with sinus rhythm, respectively (p=0,001); on the left — 1,59±0,55 and 1,22±0,43 cm2 in the group with AF and in the control group, respectively (p=0,01). Moreover, time-averaged maximum (TAMAX) and mean (TAMEAN) velocities of IJVs in the AF group were significantly lower than in patients with sinus rhythm (on the right, TAMAX was 7,86±2,32 and 12,48±6,15 cm/sec in the AF group and in the control group, respectively (p=0,01); on the left — 7,40±2,35 and 11,37±5,24 cm/sec in the AF group and in the control group, respectively (p=0,01); on the right, TAMEAN was 4,82±1,65 and 7,70±3,22 cm/sec in the AF group and in the control group, respectively (p=0,01); on the left — 4,42±1,58 and 7,25±3,10 cm/sec in the AF group and in the control group, respectively (p>0,01). However, the velocity characteristics in the AF group remained within the lower reference limit. Similar velocity values by groups were obtained regarding basal veins of Rosenthal.
Conclusion. Evaluation of the geometric and hemodynamic characteristics of the IJV during a comprehensive ultrasound examination is necessary in patients with AF, since they are characterized by dilated IJV and decreased velocity parameters to lower reference limit. The ultrasound data of the IJV in patients with AF reflect the initial signs of venous outflow impairment. This can lead to an increase in peripheral resistance in the arterioles, and as a consequence, to impaired cerebral perfusion and cognitive dysfunction.
STUDIES AND REGISTERS
What is already known about the subject?
- The clinical phenotype of patients with atrial fibrillation and heart failure (HF) is characterized by a higher risk of cardiovascular events and death.
- These patients require prevention of thromboembolic events and the appointment of optimal disease-modifying therapy to reduce the progression of structural and functional cardiac remodeling and the risk of adverse events.
What might this study add?
- The prescription rate of anticoagulant therapy in certain Russian regions in patients with atrial fibrillation and HF in 2023 was 77,8%. Only 17,4% of patients with HF with reduced and mildly reduced left ventricular ejection fraction received 4-agent disease-modifying therapy.
Aim. Retrospective analysis of the prescription rate of anticoagulant and disease-modifying therapy (DMT) to patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and heart failure (HF) in certain Russian regions as of December 31, 2023.
Material and methods. A group of patients with AF and HF (n=7901, men 51,1%, mean age 72,4±11,3 years, mean CHA2DS2-VASc (congestive heart failure, hypertension, age ≥75 years, diabetes mellitus, stroke, vascular disease, age 65 to 74 years, sex category) score 4,1±1,5) was formed based on data from the Webiomed predictive analytics platform and presented by depersonalized formalized data extracted using continuous sampling from electronic health records of patients aged ≥18 years in 22 Russian regions.
Results. The anticoagulation prescription rate in the whole sample was 77,8%, while the proportion of direct oral anticoagulants was 72,9%. With CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥2 in men and ≥3 in women, anticoagulant therapy was prescribed in 77,9%. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers were prescribed in 84,0% (valsartan+sacubitril — in 10,3%), β-blockers — in 80,2%, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists — in 60,4%, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors — in 13,9%. In the subgroup of individuals with reduced and mildly reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, 4-agent DMT was received by 17,4%, 3-agent — by 42,6% of patients.
Conclusion. Despite the positive changes in anticoagulant prescription rate and related proportion of direct oral anticoagulants for AF and HF in certain Russian regions in 2023 compared to a similar analysis for 2019 (62,5 vs 51,2%), it can still be considered inconsistent with current clinical guidelines. With a high prescription rate of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers, β-blockers and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in patients with AF and HF, there is still a low proportion of people receiving 4-agent DMT.
What is already known about the subject?
- According to a number of studies, the incidence of unstable angina (UA) in non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (ACS) has been steadily decreasing as the definition of cardiac biomarkers, primarily high-sensitivity troponin, has improved. Currently, the incidence of UA as an outcome of ACS varies significantly according to different studies.
What might this study add?
- According to the prospective registry of non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome in a regional vascular center (CONTRAST), the incidence of UA as a disease outcome significantly exceeded the incidence of non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. When making a diagnosis, doctors focused more on the clinical condition, electrocardiographic and echocardiographic abnormalities, and coronary artery involvement than on the level of troponin.
Aim. To evaluate the real-world practice of diagnosing non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) and unstable angina (UA) in patients admitted with a diagnosis of non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (NSTE-ACS) to a regional vascular center of one of the Moscow region cities.
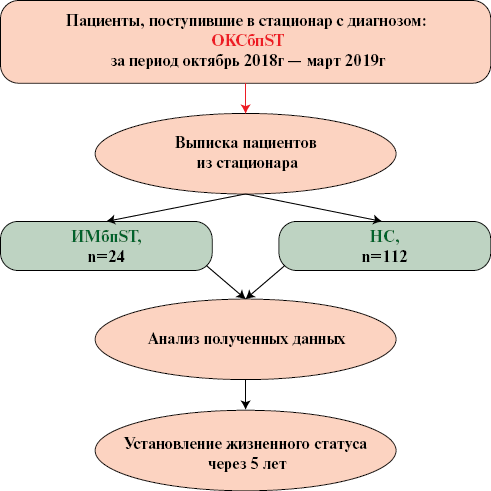
Material and methods. The prospective registry of NSTE-ACS in a regional vascular center (CONTRAST) included all patients consistently admitted with a diagnosis of NSTE-ACS from October 2018 to March 2019. Upon admission, all patients underwent coronary angiography (CAG). Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was considered depending on the CAG data, as well as the clinical condition of the patients, electrocardiographic and medical history data. At the time of CAG and the decision for PCI, the blood troponin levels were unknown.
Results. The study included 136 patients, of whom 83 (61%) were men. The mean age of patients was 63,8±10,9 years, ranging from 38 to 93 years. At hospital discharge, UA was diagnosed in 112 (82,4%) patients and NSTEMI — in 24 (17,6%). UA was more common in female patients than NSTEMI — 40,2 vs 33% (p>0,05). NSTEMI, on the contrary, was more common in males — 66,7 vs 59,8% (p>0,05). Patients with NSTEMI were older than patients with UA — 69 years vs 63 years (p=0,011). Patients with NSTEMI were significantly more likely to have a prior MI — 58 vs 32% (p=0,029). According to angiographic data, patients with NSTEMI demonstrated a higher prevalence of multivessel coronary artery disease — 50 vs 26,8% (p=0,041). Predominantly in patients with NSTEMI, an increase in the troponin I level was observed — 83 vs 50% (p=0,011). In patients with UA, emergency PCI was performed significantly less frequently compared to patients with NSTEMI — 28 vs 67% (p=0,001). When prescribing dual antiplatelet therapy in a hospital, ticagrelor was preferred as the second drug in patients with NSTEMI — 50 vs 10% (p<0,001), while in patients with UA, on the contrary, clopidogrel was used more often — 84 vs 50% (p<0,001).
Conclusion. The results suggest that when making a definitive diagnosis, doctors were more focused on the medical history, the clinical condition of patients, ECG and echocardiography abnormalities, and the severity of CAG changes. Data on cardiac specific troponin levels were less often considered.
PUBLIC HEALTH, ORGANIZATION AND SOCIOLOGY OF HEALTHCARE, MEDICAL AND SOCIAL EXPERTISE
What is already known about the subject?
- Overweight and obesity are key modifiable risk factors (RFs) for noncommunicable diseases, including cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes.
- The effectiveness of preventing noncommunicable diseases directly depends on reducing overweight and modifying behavioral RF, including nutrition and physical activity.
- Despite the proven effectiveness of behavioral interventions, the results often remain insufficient due to low patient compliance and limited monitoring by health workers.
What might this study add?
- This study represents the first experience of assessing changes in behavioral RFs during remote monitoring without the participation of a health professional providing in-depth preventive counseling.
- The data obtained can contribute to the further development and adaptation of digital preventive solutions for self-monitoring of bodyweight and modification of behavioral RFs.
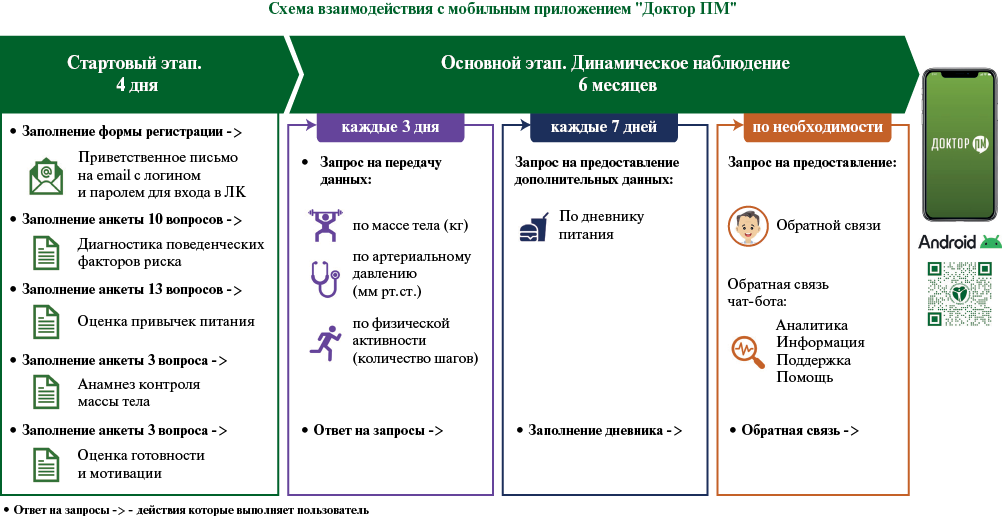
Aim. To evaluate the effectiveness of digital technologies for remote monitoring of modifying behavioral risk factors for excess body weight among students without chronic diseases.
Material and methods. The study included 38 Pskov State University medical students without chronic diseases with a body mass index >25 kg/m2 who underwent a preventive examination. Behavioral risk factors (unhealthy diet, insufficient exercise) were modified using the Doctor PM mobile application without the involvement of medical professionals. Questionnaires (active links in the mobile app) were used to assess the attitude and opinion of users towards the remote monitoring technology. The follow-up period was 6 months.
Results. Dietary habits were corrected in 77,7% of participants, including a decrease in the consumption of fats, simple carbohydrates, and salt, as well as an increase in the frequency of consumption of vegetables and fruits. Increased physical activity was noted by 71,4% of students. Body weight decreased in 65,8% of participants, of which 31,6% achieved target indicators. The majority (86,8%) rated positively the convenience and utility of personalized recommendations in the Doctor PM application.
Conclusion. The first experience of practical application of digital preventive mobile technology for remote monitoring of eating habits and physical activity, as well as support for reducing excess body weight is presented using a cohort of students without chronic diseases as an example. It is important to note that the modification of behavioral risk factors occurred without medical support. Further monitoring and indepth analysis of the results are required for scaling this technology.
What is already known about the subject?
- Ischemic heart disease (ICD) is one of the main causes of high mortality, but the contribution of chronic IHD (CIHD) to the structure of mortality due to chronic remains insufficiently studied.
What might this study add?
- In the structure of mortality from ICD in the subjects of the Russian Federation, CIHD predominates with 8-fold differences in the standardized mortality rate and even more pronounced differences in the standardized mortality rate from individual CIHD types.
- The results indicate the need to clarify the clinical criteria for individual types of CIHD.
Aim. To assess the changes and variability of standardized mortality rates (SMR) from various types of chronic ischemic heart disease (CIHD) in the Russian Federation and its regions in 2014-2023.
Material and methods. The Rosstat data analysis of CIHD mortality for 2014-2023 was carried out in accordance with the Rosstat Brief Nomenclature of Death Causes. The calculations were performed using the computer program "Calculation and Analysis of Mortality Rates and Years of Life Lost due to Premature Mortality in the Subjects of the Russian Federation". The European standard of the World Health Organization (1976) was used to calculate the SMR. The calculation of mean regional SMRs and their comparison were performed using the SPSS 26.0 program.
Results. The mean regional SMR from CIHD for 2014-2023 decreased from 205,93±67,93 to 175,81±62,36 per 100 thousand population. Regional variability of SMR from CIHD as a whole did not undergo significant changes as follows: in 2014, the maximum SMR exceeded the minimum by 8,5 times; in 2023 — 8 times. The number of regions with I25.0-I25.9 SMR of 0 increased from 8 to 19 during the analyzed period. The coefficient of variation of regional SMRs from CIHD in 2023 is higher than in 2014. No uniform trends in the SMR for all regions were recorded for any CIHD types.
Conclusion. Significant and increasing regional variability of SMR from certain CIHD types is recorded. No standardization of clinical, morphological and statistical principles for coding certain CIHD types as the underlying cause of death hinders the assessment and analysis of mortality changes. Consequently, this inhibits the development of measures to reduce them reliably and effectively. Typification of coding approaches will serve to improve the quality of analysis of CIHD mortality statistics and the subsequent adoption of targeted management decisions.
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
What is already known about the subject?
- There is known impact of such risk factors (RF) on survival, such as age, blood pressure and heart rate, blood lipid profile disorders, obesity, smoking and education status.
- The relationships between survival and RF in most cases were identified and proven using multiple linear regression.
- In medical research, the use of nonlinear statistical methods is preferable.
What might this study add?
- Using nonlinear artificial neural networks, the comparative significance of listed RFs was studied in long-term prospective follow-up of the Russian population.
Aim. To compare the significance of risk factors (RF) in neural network modeling of a fatal outcome for prospective follow-up periods of 10, 20, 30 and 40 years.
Material and methods. From the Russian Lipid Research Clinics Study of 1975-1982, 13263 men and 5691 women were included in the current follow-up until 2017. The end point was all-cause death. Sex, age, blood pressure, heart rate, body mass index, blood lipid levels, smoking and education status, hypertension and hypotension were analyzed. Artificial neural network simulators were used to build multivariate models.
Results. According to the sensitivity analysis, the significance of all input variables included in the models increases with follow-up duration extension. The minimum significance of studied risk factors is observed with a 10-year follow-up in women.
Conclusion. Neural network prediction of a fatal event using the studied risk factors reaches maximum information content by 30 years of prospective follow-up.
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROBLEMS IN CARDIOLOGY
What is already known about the subject?
- Cardiotoxicity is a known effect of chemotherapy (CT); protocols for the prevention, monitoring and treatment of this complication have been published. The vascular toxicity of chemotherapy and methods for its diagnosis remain unexplored. Arterial stiffness appears to be a promising marker of potential vasculotoxic reactions.
What might this study add?
- Arterial stiffness was studied using various methods in patients with breast cancer receiving combination chemotherapy, including anthracyclines.
- An increase in carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity was found 12 months after the start of chemotherapy when compared with initial values, indicating accelerated vascular aging in this category of patients.
Aim. To identify and analyze changes of arterial stiffness (AS) parameters in breast cancer patients undergoing combination anthracycline-containing chemotherapy (ACCT).
Material and methods. Fifty women with verified breast cancer aged 46,7±7 years with indications for combined ACCT were assessed for AS (carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity (cfPWV) (m/s); cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI); cardio-ankle pulse wave velocity (caPWV) (m/s); β-stiffness index, novel Russian Stelari and haStart indices) at 4 visits as follows: before ACCT, after 8-12, 20-24 and 48 weeks from the ACCT start.
Results. A reliable decrease in cfPWV was revealed at visit 2 (7,48±1,51, p<0,05) and visit 3 (8,34±1,66, p<0,05) with further significant increase at visit 4 when compared with baseline data. Similar reliable changes were demonstrated for the Stelari index. CAVI decreased at visits 2 and 3 with a reliable difference from the values at visits 1 and 4. No reliable changes in β and haStart stiffness indices were obtained during the follow-up period.
Conclusion. In patients with breast cancer who underwent combined ACCT, an increase in cfPWV by 0,95 m/s per year was revealed, which indicates accelerated vascular wall aging and a possible increase in cardiovascular risk in this category of patients.
EXPERT CONSENSUS
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)