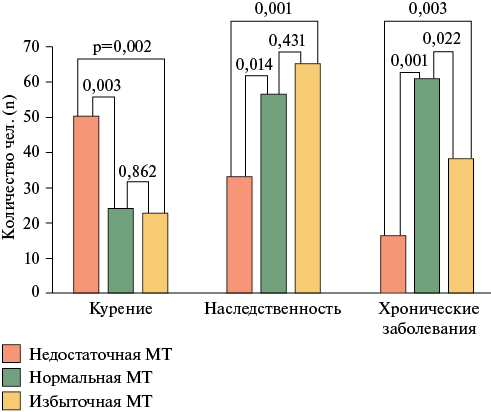MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
What is already known about the subject?
- The main disadvantage of X-ray angiography in endovascular treatment of patients with acute myocardial infarction is the inability of direct plaque imaging.
- Studies have shown a weak correlation between angiographic and histological data.
- Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) may be considered as a better alternative.
What might this study add?
- IVUS during percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute myocardial infarction can improve immediate and long-term outcomes.
- The cost per year of life gained due to the use of IVUS during percutaneous coronary intervention was determined.
Aim. To determine the number of years of lost life (YLL) as a result of not using intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) during percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), as well as to conduct a costeffectiveness analysis.
Material and methods. This randomized controlled study included 431 patients with acute STEMI treated at the Department of X-ray Surgical Diagnostic and Treatment Methods of the Vsevolozhsk Clinical Interdistrict Hospital. Patients of the first group (n=161) underwent IVUS-guided PCI, while patients of the second group (n=270) — angiography-guided PCI. The inclusion criterion was electrocardiographic changes corresponding to acute STEMI, followed by coronary angiography confirmation. Patients with cardiogenic shock were excluded from the study due to expected higher rates of inhospital and one-year mortality compared to patients with acute STEMI without cardiogenic shock. Traditional life tables were constructed, and an analysis of differences in death probability within one year after surgery was performed. A model was constructed showing the number of lives could have been saved if all patients in the PCI angiography group had been supplemented with IVUS. The number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one adverse outcome and the cost of life-years saved due to the implementation of IVUS were calculated.
Results. Not using IVUS for coronary artery stenting in patients with acute STEMI (n=270) potentially results in YLL losses of 117,3 personyears. The number of patients who need to be treated to prevent one adverse outcome was 12,9 (95% confidence interval: 7,3-104). The cost of one saved person-year of life for the regional Ministry of Health was RUB 195 666 in the analyzed period. At the same time, the increase in costs for one additional life saved during the year is RUB 1 105 000.
Conclusion. IVUS in patients with acute STEMI has high economic potential and social orientation in a long-term analysis.
What is already known about the subject?
- In patients with myocardial infarction (MI), delirium occurs in 1,4-13% of cases.
- Delirium in patients with MI increases the duration of hospitalization and is associated with an increase in mortality.
- There is evidence of the role of systemic hemodynamic disorders in the development of delirium, leading to cerebral hypoxia.
What might this study add?
- Delirium in MI develops predominantly in individuals >69 years old with a left ventricular ejection fraction <45%.
- The Gensini score, reflecting the severity of coronary atherosclerosis, is on average 1,4 times higher in patients with delirium than in patients without delirium, and 1,7 times higher in the group of individuals >75 years old (80,0 vs 48,0).
Aim. To compare clinical characteristics and severity of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with myocardial infarction (MI) with and without delirium.
Material and methods. The registry of 2537 patients with MI hospitalized in 2023 in the Tver Regional Clinical Hospital was analyzed. Delirium was diagnosed in 58 patients (2,3%) who were included in group 1, and 2479 patients without delirium from group 2. The Gensini score was calculated in 53 patients with delirium (main group) and 106 patients without delirium, included in the comparison group by selecting age-matched pairs.
Results. Patients in group 1 were on average older than patients in group 2 (76,0 vs 66,0 years, p<0,001), they had a lower left ventricular ejection fraction (43,0 vs 46,0%, p<0,001), more often developed stroke during hospitalization (8,6 vs 1,4%, p<0,001) and death (17,2 vs 6,4%, p=0,001). The main and control groups were comparable in all variables taken into account, with the exception of Gensini score. Mean Gensini score was higher in the main group than in the control group — 64,0 vs 46,0 (p=0,002).
Conclusion. Delirium in MI develops mainly in people >69 years old with an ejection fraction <45%. Coronary atherosclerosis in patients with MI with delirium is, on average, more pronounced than in patients without mental disorders.
CORONARY HEART DISEASE
What is already known about the subject?
- Stress echocardiography (SE) is indicated for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease with a high recommendation class.
- The multi-stage ABCDE protocol can provide important additional information.
What might this study add?
- The use of ABCDE-SE protocol with exercise allows risk stratification of patients with confirmed and suspected coronary artery disease.
- Additional parameters of ABCDE SE protocol can improve the diagnostic value of exercise testing.
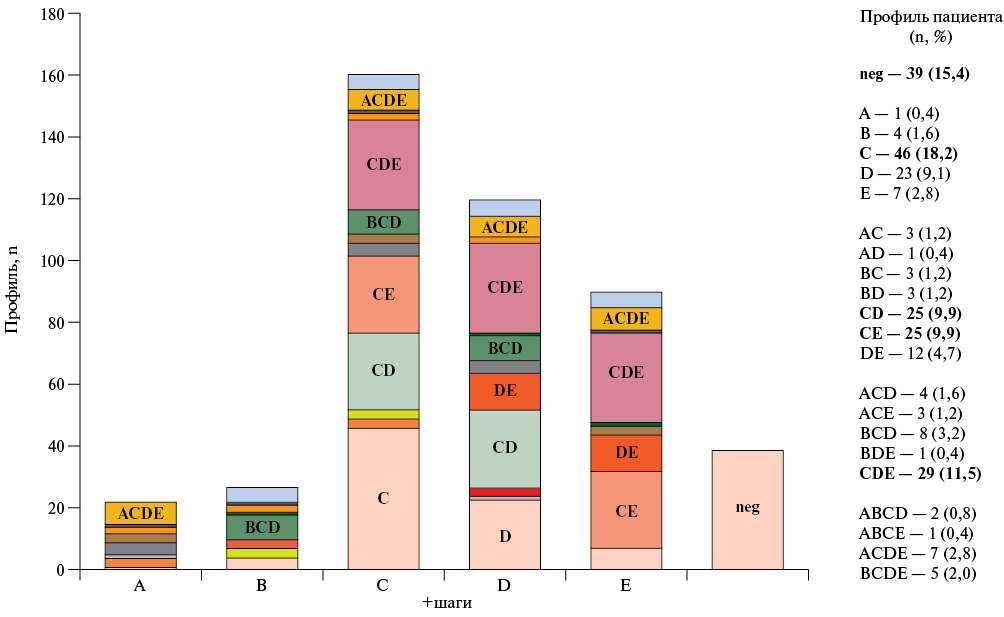
Aim. To assess the role of stress echocardiography (SE) parameters according to ABCDE protocol as predictors of cardiovascular events (CVD).
Material and methods. This single-center prospective study included 253 patients (men n=130, 51,4%; median age, 62 (53; 68) years) with confirmed (14,2%) and suspected coronary artery disease (CAD). Exercise SE was performed according to clinical indications. The ABCDE protocol included assessment of regional wall motion (step A), B-lines (step B), contractile (step C), coronary (step D), chronotropic (step E) reserves of the left ventricle. The median follow-up period was 198 (118; 324) days. Twenty one (8,3%) patients underwent revascularization, while 11 patients (4,4%) were rehospitalized for cardiovascular events. The influence of clinical and echocardiographic parameters on endpoints was assessed.
Results. The incidence of abnormal SE results was 8,7% (n=22) for step A, 10,7% (n=27) for step B, 63,6% (n=161) for step C, 47,4% n=120) for step D, and 35,6% (n=90) for step E. An independent predictor of readmission was the ACDE profile (a combination of positive SE steps) (odds ratio, OR 22,4; p=0,003); predictors of revascularization were the ABCDE score (OR 24,4; p=0,005), chest pain pattern (OR 7,2; p=0,005), DE profile (OR 762; p=0,003), chronotropic reserve (OR 437; p=0,019), number of risk factors (OR 7,7; p=0,009).
Conclusion. ABCDE protocol SE allows for a comprehensive assessment of heart functional status, improves the diagnostic ability of stress test, and identifies predictors of cardiovascular disease in patients with suspected and confirmed CAD.
What is already known about the subject?
- Statins have a positive effect on myocardial flow parameters according to positron emission tomography and single-photon emission computed tomography in patients with obstructive coronary artery disease.
What might this study add?
- The positive effect of combination therapy (statins+antianginal agents) on left ventricular myocardial perfusion in patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease has been demonstrated.
Aim. To study the potential of assessing left ventricular (LV) myocardial perfusion using volumetric computed tomography (VCT) with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) test in patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease (NOCAD) during combined therapy.
Material and methods. Cardiac VCT with ATP test, combined with computed coronary angiography, was performed in 46 patients with an established diagnosis of NOCAD. At the time of enrollment, all patients were recommended lipid-lowering therapy to achieve target lipid profile parameters, antianginal and antithrombotic therapy.
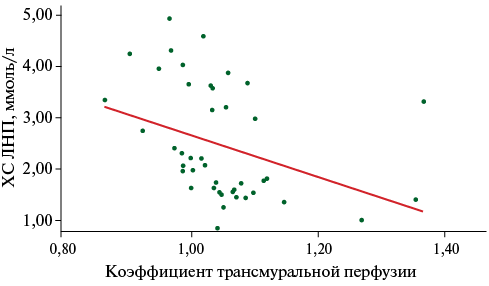
Results. Changes of LV myocardial perfusion parameters depending on achievement of target low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) demonstrates reliable decrease in the number of LV myocardial segments with perfusion defects (2 [0; 3] vs 6 [3; 8], p<0,001) and increase in transmural perfusion coefficient (TPC) in the stress phase (1,14±0,12 vs 1,02±0,07, p=0,004). Moderate negative correlation was revealed in patients with NOCAD between the mean TPC value in the stress phase and LDL-C level (n=45, rho=-0,56; p=0,001). Significant improvement of LV myocardial perfusion was demonstrated among patients receiving combination therapy.
Conclusion. Combination therapy is significantly associated with improved LV myocardial perfusion parameters. When the target LDL-C level is reached, it is accompanied by a significant TPC increase and a decrease in the number of segments with perfusion defects in patients with NOCAD according to VCT with an ATP test.
HEART FAILURE
What is already known about the subject?
- Left ventricular assist device (LVAD) implantation is an effective method for treating end-stage heart failure when heart transplantation is not possible.
What might this study add?
- Despite complications, LVAD implantation decreased hospitalization rate, improved quality of life and functional capabilities of patients.
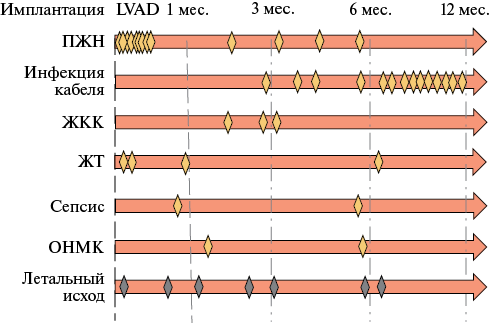
- Following chronological relationship of complications was found: in the first 6 months, right ventricular failure, gastrointestinal bleeding, ventricular tachycardia occurred, and later — LVAD-associated infection.
- This study failed to reduce mortality. It is necessary to improve the selection of patients and their postoperative monitoring.
Aim. To study hemodynamic changes according to transthoracic echocardiography, heart failure (HF) course, quality of life (QOL) of patients, complications and mortality within 12 months after implantation of a left ventricular assist device (LVAD).
Material and methods. The study included 53 patients with endstage HF who met the criteria for LVAD implantation. Group 1 included 23 patients who underwent implantation, while group 2 included 30 patients who refused the intervention. At baseline, before discharge, and after 3, 6, and 12 months, the following were performed: transthoracic echocardiography, 6-minute walk test, assessment of HF class, quality of life, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, hospitalization rate, complications, and fatal outcomes.
Results. Mortality in group 1 was 30,4%, and in group 2 — 30,0%. The following complications of LVAD implantation were recorded: right ventricular failure — 13, gastrointestinal bleeding — 3, ventricular tachycardia — 4, LVAD-associated infection — 14 cases. Unlike group 2, in group 1, we recorded decrease of LV end-diastolic dimension from 7,4 [7,1; 8,0] to 6,4 [5,7; 6,9] cm (p<0,001), mitral regurgitation from 2,2±0,54 to 1,44±0,4 st, (p<0,001), N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide from 2239 [1623; 4057] to 740 [438.5; 1273] pg/ml (p<0,001), as well as improvement of HF class (p<0,001), and lower hospitalization rate — 23 vs 37 (p=0,014).
Conclusion. In the present study, LVAD implantation improved intracardiac hemodynamics, HF class, quality of life, as well as decreased the hospitalization and HF decompensation rates, but not a mortality.
What is already known about the subject?
- Diastolic stress test in combination with cardiopulmonary exercise testing allows for a more accurate diagnosis of heart failure with preserved left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (HFpEF).
- The main diagnostic criteria are an increase in ratio of the peak velocity of early diastolic transmitral flow to early diastolic rise of LV base ≥15, an increase in peak tricuspid regurgitation velocity >3,4 m/s.
What might this study add?
- In obese patients, initial diastolic dysfunction was observed under a load of 50 W, which also persisted during the recovery period.
- Evaluation of tissue Doppler velocity parameters (septal and lateral e’) made it possible to identify a decrease in LV systolic function with an increase in load above the anaerobic threshold in patients with HFpEF, whereas in groups of patients with normal or slightly reduced body weight and hypertension and patients with hypertension and obesity, these parameters continued to increase.
- The use of transthoracic 2-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography made it possible to identify early signs of impaired systolic and diastolic LV function during exercise and made it possible to suspect the subclinical course of HFpEF.
Aim. To evaluate the potential of cardiopulmonary exercise testing in combination with exercise stress echocardiography in detection of heart failure (HF) with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in patients with hypertension (HTN) and obesity.
Material and methods. The observational study included 150 patients with HTN, of which 35 were without obesity and had no signs of HF, 35 — with obesity and without signs of HF, while 80 had signs of HFpEF and obesity. Hypertension was considered detected with office blood pressure ≥140/90 mm Hg, while obesity — with a body mass index ≥30 kg/m2. Patients underwent resting and exercise echocardiography, and the parameters of systolic and diastolic left ventricular (LV) function were analyzed. During the diastolic stress test, LV diastolic function was assessed at 50 W, upon reaching the anaerobic threshold (AT), submaximal heart rate, and during the recovery period.
Results. The mean age of patients was 58,2±10,8 years. Changes of tissue Doppler parameters in patients with HFpEF showed significantly lower septal and lateral mitral annulus velocity (e’) at all exercise stages, compared with other groups. At the same time, septal and lateral e' increased as AT was reached, and a further exercise increase was not accompanied by an increase in these parameters at the level of submaximal heart rate.
Conclusion. The combination of diastolic stress test with cardiopulmonary testing made it possible to identify a decrease in LV systolic function with a load increase above AT in patients with HFpEF, while in other groups these parameters continued to grow. These parameters can be used in the diagnosis of HFpEF with an inconclusive increase in the ratio of the peak velocity of early diastolic transmitral flow to early diastolic rise of LV base (E/e’) at a low exercise level.
RISK FACTORS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
What is already known about the subject?
- Breast arterial calcification (BAC) is a form of medial calcification distinct from intimal calcification associated with atherosclerosis.
- BAC is considered as a promising marker of female-specific cardiovascular risk.
- There are conflicting data on the association of BAC with traditional cardiovascular risk factors, such as dyslipidemia, inflammation, obesity, smoking, and reproductive function parameters.
What might this study add?
- For the first time in Russian women, we revealed a significant association of BAC with reproductive function parameters (postmenopause, breastfeeding, number of pregnancies), as well as with lower anthropometric parameters and higher blood pressure.
- No association with lipid, carbohydrate metabolism parameters and inflammation were revealed.
- It can be assumed that the leading pathogenetic mechanism for cardiovascular disease development in individuals with BAC is increased vascular stiffness.
Aim. To study the association of breast arterial calcification (BAC) with reproductive history and cardiovascular risk factors (RFs).
Material and methods. A total of 198 women aged 40-74 years were examined. The groups with/without BAC were formed according to the case-control method in a 1:1 ratio taking into account age. Medical history, reproductive function, cardiovascular risk factors, clinical and paraclinical parameters were assessed.
Results. Women with BAC were more often postmenopausal than women without BAC (p=0,032), had a higher breastfeeding prevalence (p=0,033), lower values of weight (p=0,001), height (p<0,001), and waist circumference (WC) (p=0,004), and higher blood pressure (BP) (p<0,05). In univariate regression analysis, BAC was associated with postmenopause, breastfeeding, a higher number of pregnancies, lower height, WC, and systolic BP. In multivariate analysis, BAC was significantly associated with height (p=0,011), WC (p=0,001), and systolic BP (p=0,003). Women without BAC were more likely to have former smoking (p=0,032). No associations of BAC with lipid and carbohydrate metabolism parameters or inflammation were found.
Conclusion. The results demonstrate an association of BAC with only some of the known cardiovascular RFs as follows: blood pressure, postmenopause, and breastfeeding, which has a protective effect on cardiovascular diseases. BAC may be considered as a promising marker of female-specific cardiovascular risk with regulatory mechanisms different from atherogenesis processes.
What is already known about the subject?
- Increased common carotid intima-media thickness and vascular stiffness have a predictive potential for various cardiovascular events.
What might this study add?
- In young adults with overweight and obesity, compared to their normal-weight peers, blood pressure and common carotid intima-media thickness are increased, but the level of vascular stiffness is reduced.
- Among young people with overweight and obesity, there are multidirectional changes of large arteries.
- The existing medical examination system for young people should be optimized in terms of wider and earlier implementation of comprehensive angiology screening.
Aim. To assess the influence of body mass index (BMI) in young people on the carotid intima-media thickness (IMT), cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI), ankle-brachial index (ABI) and some cardiovascular risk factors.
Material and methods. The study included 171 young people (75 males and 96 females) aged 18-25 years. All subjects were divided into 3 following groups depending on their BMI level: group 1 — underweight, group 2 — normal weight, group 3 — overweight and obesity. In these groups, we determined the common carotid IMT using the RuScan 70P ultrasound system (NPO Scanner, Russia), the CAVI and ABI values using the Vasera VS-1500 system (Fukuda Denshi, Japan), as well as blood pressure (BP) and main cardiovascular risk factors.
Results. An association between BMI and left carotid IMT was revealed both among young men and among young women (ANOVA, p=0,023 and p1-2=0,049). The ABI on the left (ANOVA, p=0,006) and CAVI (ANOVA, p=0,001 on the right and p=0,001 on the left) in young women were significantly higher in the 1st group compared to the 2nd and 3rd groups. The highest systolic BP is observed in the overweight and obesity group compared to the normal and underweight groups both among young men (p1-3=0,002 and p2-3=0,015 on the right and p1-3=0,002 and p2-3=0,009 on the left) and among young women (p1-3=0,024 and p2-3=0,023 on the left and p1-2=0,032, p1-3=0,003 and p2-3=0,042 on the right), respectively.
Conclusion. Early vascular remodeling in young people associated with overweight and obesity is characterized by higher IMT values in combination with physiological adaptation of large arterial media in the form of lower arterial stiffness in response to the training effect of overweight/obesity in this age period.
What is already known about the subject?
- Increased body weight is an important modifiable risk factor for cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular and all-cause death.
What might this study add?
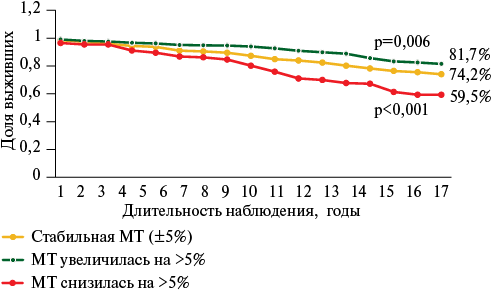
- Previous unintentional decrease in body weight by more than 5% is associated with a significant increase in the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause death, while an increase by >5% is associated with improved survival.
- When assessing the cardiovascular and all-cause death risks, not only the current body weight should be taken into account, but also the previous direction of its changes.
Aim. To study the influence of body weight changes as a factor determining the risk of cardiovascular and all-cause death in a 34-year prospective follow-up of a Tomsk population cohort.
Material and methods. This 34-year prospective study included 1546 people aged 20-59 years. In 1988-1991, anthropometric measurement and calculation of body mass index were performed, while in 20022005 — re-examination of the cohort with body weight assessment. In 2022, we studied the effect of body weight changes on cardiovascular and all-cause mortality.
Results. Prior body weight decreases by more than 5% is accompanied by an increase in all-cause death risk by 1,6 times compared to individuals with stable weight, and 2,3 times higher compared to those with body weight increased during the follow-up period. Cardiovascular death risk in the case of body weight decrease is 1,7 and 3 times higher, respectively. The best 17-year survival was established among individuals with an increase who had an increase in BW by more than 5%.
Conclusion. A decrease in body weight by more than 5% is an independent predictor of cardiovascular and all-cause death. When assessing the cardiovascular and all-cause death risks, not only the current body weight should be taken into account, but also the previous direction of its changes.
CLINICAL CASE
- Due to the small number of cases, approaches to the treatment of pregnant women with floating right heart thrombi have not been sufficiently studied and require an alternative approach to minimize perioperative risks.
- A case of floating right atrial thrombosis in a pregnant patient with genetic thrombophilia and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary endarterectomy is described.
- Transesophageal echocardiography-guided indirect transjugular thrombectomy using the TREX thromboextractor made it possible to achieve favorable technical and clinical success.
Floating thrombus in right heart indicates a high probability of pulmonary embolism, which can lead to severe consequences, including sudden death. Floating right heart thrombi in pregnant women are a rare but potentially dangerous complication that requires immediate treatment. The management of such patients requires an individual multidisciplinary approach taking into account the patient’s condition and thrombus characteristics. This article presents a case of successful thrombectomy in a 26-year-old patient in the second trimester of her second pregnancy with floating right atrial thrombosis. This case is unique due to the combination of following risk factors for thrombosis: pregnancy, genetic thrombophilia, and prior chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension with pulmonary endarterectomy. A special feature of this case is successful indirect transjugular thrombectomy with echocardiography guidance as a less invasive alternative to open surgery or angiography-guided endovascular intervention, which minimized the risks of complications and achieved a favorable outcome. However, adherence to the proper interbirth interval and optimal anticoagulant prophylaxis in pregnancy would reduce the risks of thromboembolic events.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about the subject?
- Microcirculatory disorders play a key role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), including coronary artery disease and hypertension.
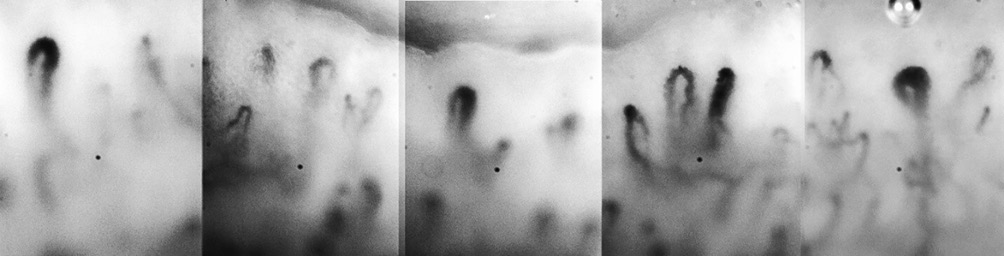
- Capillaroscopy makes it possible to evaluate the structural and functional parameters of capillaries, but requires standardization.
- A decrease in capillary network density correlates with the risk of cardiovascular events, such as myocardial infarction and organ dysfunction.
What might this study add?
- The study emphasizes the clinical significance of capillaroscopy for early diagnosis of microcirculatory disorders in patients with CVD.
- Artificial intelligence algorithms for analyzing capillaroscopy data should be implemented.
- Prognostic value of capillary system changes as markers of disease progression is showed.
The development and progression of cardiovascular diseases is accompanied by various changes at all vascular levels, from large arteries to capillaries. This makes it especially important to study various approaches to diagnosing vascular lesions. Particular attention is drawn to non-invasive research methods that have wide potential for assessing microcirculatory disorders. Of greatest interest is capillaroscopy, which can be used to assess both structure and function. The article discusses the current status of microcirculation assessment and the potential of capillaroscopy in diagnosing various disorders in patients with cardiovascular disease.
What is already known about the subject?
- Early vascular aging (EVA) is one of the leading causes of coronary artery disease in young people.
- The main characteristics of EVA include increased vascular stiffness and short telomeres.
What might this study add?
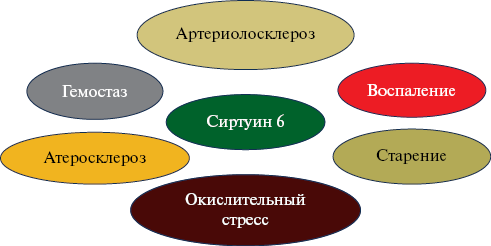
- Sirtuin 6, which is involved in the regulation of inflammation, oxidative stress, atherogenesis and a number of other processes associated with aging and cardiovascular diseases, may become a promising therapeutic target for EVA.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains the leading cause of disability and high mortality, including among working-age people. One of the most common causes of CAD in young people is early vascular aging (EVA). Studying the regulatory role of sirtuin 6 in the development of EVA seems relevant. The purpose of the review was to analyze the literature data on the possible influence of sirtuin 6 on EVA in young and middle-aged patients with CAD. For this purpose, we searched data in international (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science and Cochrane Library) and Russian (eLIBRARY and CyberLeninka) databases. Particular attention was paid to works published over the past 15 years, with an emphasis on studies conducted over the past 5 years. Literature analysis showed that sirtuin 6, epigenetically modulating gene transcription and changing protein function, is involved in the main mechanisms of aging and related cardiovascular diseases. Thus, studying the effects of sirtuin 6 will provide a more detailed understanding of complex interaction, systemic factors and the development of cardiovascular pathology.
What is already known about the subject?
- Anemia is one of the most common concomitant conditions in patients with heart failure (HF).
- Anemia is a unfavorable prognostic factor in relation to mortality and hospitalizations in HF.
What might this study add?
- We present modern views on clinical associations and prognostic significance of anemia taking into account the left ventricular ejection fraction.
- The article considers not only the treatment of anemia in HF, but also HF features that must be taken into account against the background of anemia.
Noncommunicable diseases are called the epidemic of the 21st century. Heart failure (HF) is one of them. Among the diseases concomitant to HF, anemia is one of the most common. It is known that HF and anemia as separate conditions can be treated at the outpatient stage. However, their combination is a serious problem. The review presents current view on anemia etiology in HF, their pathogenetic relationship, clinical associations and prognostic significance of anemia in HF, as well as methods for treating anemia against the background of HF and some features that should be taken into account during HF treatment in patients with anemia.
CONSENSUS OF RUSSIAN EXPERTS
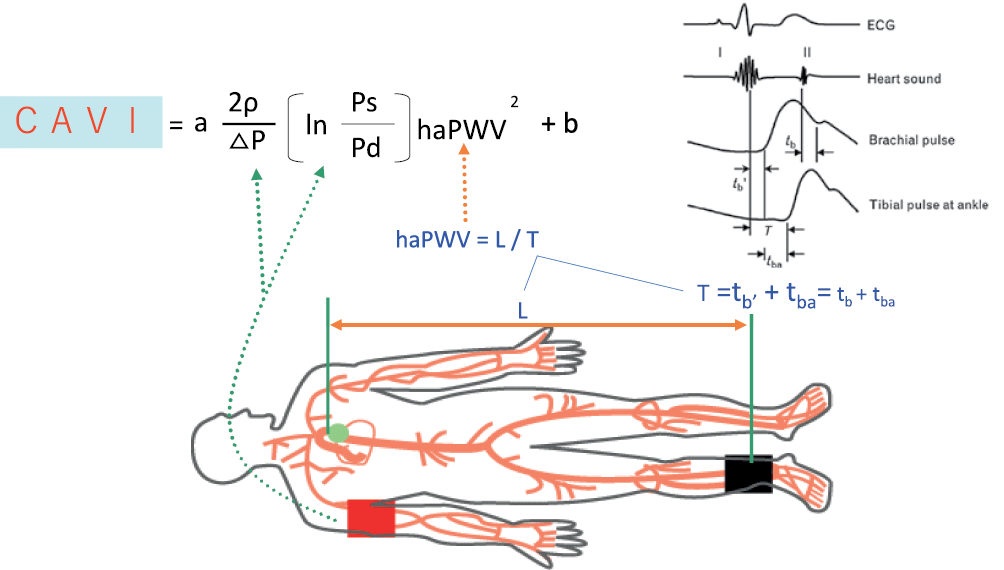
Arterial stiffness measured using carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity is an independent predictor of cardiovascular mortality and is recommended as a reference standard. Cardio-ankle index is a simple, wellstandardized, accurate and reproducible method for assessing arterial stiffness, independent of blood pressure level during measurement. The aim of this paper is to analyze and systematize new factual data, as well as develop an expert opinion on the significance of arterial stiffness diagnosis and the use of cardio-ankle index.
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)