RISK FACTORS FOR CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
What is already known about the subject?
- Research shows that psychological imbalance is associated with changes in dietary patterns.
What might this study add?
- It has been noted that individuals with depression are less likely to include animal products (red meat, fish, poultry, dairy products), vegetables/fruits in their daily diet, but are more likely to consume processed foods high in salt and calories.
- The dietary patterns of individuals with depression are not influenced by age or regional characteristics and show sex differences only in the consumption of certain foods (fish, poultry, sweets).
Aim. To study the associations between depression and dietary patterns, including alcohol consumption, in the Russian population.
Material and methods. Representative samples of men and women aged 25-64 (n=22217, 8519 men, 13698 women) from 13 Russian regions were surveyed. The response rate was approximately 80%. Dietary patterns were assessed based on the consumption rate of key food groups. Depression was assessed using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), with the following criteria: 0-7 — no depression, 8-10 — subclinical depression, and ≥11 — clinical depression. Results are presented as percentages, odds ratios (OR), and 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Results. Depression in both men and women reduces the consumption of natural foods. Men and women, regardless of depression severity, reduce their consumption of dairy products, as well as vegetables and fruits (p<0,05). Men and women with clinically significant depression reduce their red meat consumption (OR 0,78, CI: [0,63-0,97] (p=0,0283) and OR 0,76, CI: [0,65-0,88] (p=0,0004), respectively). Women with clinically significant depression consume sweets less often in their diet than healthy women (OR 0,84, CI: [0,73-0,97] (p=0,018)). Excessive salt intake is more common in the diet of individuals with depression than in healthy ones. A higher frequency of adding extra salt to food was observed in men (OR 1,35, CI: [1,16-1,57] (p<0,001) and OR 1,28, CI: [1,03-1,6] (p=0,027)) and women (OR 1,36, CI: [1,22-1,52] (p<0,0001) and OR 1,47, CI: [1,27-1,7] (p<0,001)) with subclinical and clinical depression, respectively. Among individuals with subclinical depression, an increase in the consumption of processed foods (pickles in men and meat and sausage products in women) was noted (p<0,05). As depression worsened in individuals of both sexes, alcohol consumption decreased both in frequency and quantity.
Conclusion. The dietary patterns of individuals with depression significantly differ from those of healthy individuals. Individuals with depression are less likely to include animal products (red meat, fish, poultry, dairy products), vegetables/fruits, and sweets in their daily diet, but are more likely to consume processed foods high in salt and calories.
What is already known about the subject?
- Coronary artery disease remains the leading cause of death in Russia.
- A link between adiponectin levels and cardiovascular disease has been demonstrated, as well as associations between ADIPOQgene variants and cardiovascular disease risk.
What might this study add?
- The GA and CA haplotypes of the ADIPOQ rs266729/rs182052 variants are associated with coronary artery disease and can be used to assess its risk in Russian population.
Aim. To validate previous findings on the association of the rs266729 and rs182052 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the ADIPOQ gene with the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) using an independent sample.
Material and methods. The study included a sub-cohort of patients (n=874) from the Vologda, Omsk, Krasnoyarsk and Primorsky Regions of the ESSE-RF population study and a sample of patients (n=258) from the biobank collection of the National Medical Research Center for Therapy and Preventive Medicine.
Results. We revealed significant association of the alternative C allele of the rs266729 SNP in a recessive univariate model with an increased risk of CAD (odds ratio (OR)=2,008, p=0,014). Based on the analysis of the rs266729 and rs182052 SNPs, four following haplotypes were identified: CG (48,2%), GA (29,0%), CA (12,6%), and GG (10,2%). Associations of the GA haplotype (OR=2,086, p=0,010) and CA haplotype (OR=4,160, p=0,032) with CAD were demonstrated in a recessive multivariate model.
Conclusion. The GA and CA haplotypes of the ADIPOQ rs266729/ rs182052 SNPs are associated with CAD and can be used to assess the CAD risk in Russian population.
КАРДИОРЕАБИЛИТАЦИЯ
What is already known about the subject?
- Reduced functional capacity and exercise tolerance in patients with heart failure is determined by a combination of cardiac and non-cardiac factors.
What might this study add?
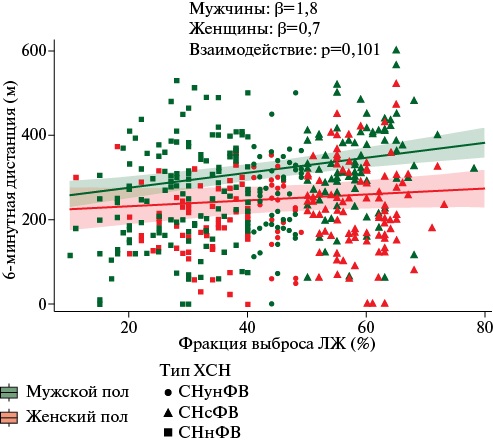
- Separately analysis for men and women showed that only age and severe anxiety/depression according to the EuroQol Group EQ 5D demonstrated an independent association with 6-minute walk test distance in women.
- In men, left ventricular ejection fraction, red blood cell volume deviation and N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide also demonstrated an independent association.
- A sex-modifying effect on 6-minute walk distance was demonstrated only for self-assessed mental state in men, in whom even moderate psychological impairment was associated with a distance reduction.
Aim. To determine cardiac and non-cardiac factors associated with exercise tolerance in male and female patients with heart failure (HF).
Material and methods. This retrospective analysis included 498 patients (198 women) with HF from the cohort of the multicenter study "Prevalence of Iron Deficiency in Patients with Heart Failure in the Russian Federation." The relationship between anthropometric, clinical, and laboratory parameters, as well as self-rated health and mental status using the EuroQol Group EQ-5D questionnaire, and exercise tolerance (6-minute walk test (6MWT)) was assessed. Multiple linear regression analysis, including models with centered variables, was used to determine the association of various factors with the 6MWT distance.
Results. Men with a 6MWT distance in the lower tertile were older, had a lower left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF), and higher N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). They were more likely to have anemia and iron metabolism disorders. In the combined model, age, LVEF, NT-proBNP level, red blood cell (RBC) volume deviation, the transferrin saturation, moderate and severe anxiety/depression self-assessment, and female sex were significantly associated with the 6MWT distance. The model’s explained variance was 31%. In models constructed separately for men and women, age, LVEF, RBC volume deviation, NT-proBNP level, and self-rated anxiety/depression were significantly associated with 6MWT distance in men while in women — only age and self-rated anxiety/depression. In models with centered variables, a significant interaction was found only for moderate depression/anxiety in men, which was associated with a decrease in distance of 82 m, and only a 21 m decrease in women.
Conclusion. All factors, except self-reported mental status, were associated with only minimal changes in 6MWT distance. No clear statistically confirmed interaction with sex was found for NT-proBNP and LVEF. However, plot analysis suggests a more pronounced association between these indicators and 6MWT distance in men.
What is already known about the subject?
- Cognitive training in virtual reality is a new approach to cognitive rehabilitation that has proven effective in patients with stroke and age-related cognitive impairment.
- The use of multitask cognitive training in virtual reality (VR-MCT) in patients after cardiac surgery may be justified in terms of preventing impairment and restoring cognitive function.
What might this study add?
- The use of VR-MCT optimizes attention and short-term memory in patients in the early postoperative period following on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting.
- Negative factors determining the cognitive status of patients undergoing VR-MCT include patient age and low educational level, as well as the initial cognitive status, while protective factors include high perioperative concentrations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and low concentrations of brain damage markers.
Aim. To analyze the success of virtual reality-based multitask cognitive training (VR-MCT) in patients who underwent on-pump coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), based on an assessment of neuropsychological and neurochemical parameters.
Material and methods. This prospective study included 49 male patients aged 45 to 75 years who underwent on-pump CABG and had early postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Beginning 3-4 days after CABG, patients underwent daily VR-MCT (mean session count — 6,7). In addition to the standard perioperative examination, all patients underwent psychometric testing and determination of neurovascular unit (NVU) markers — neuron-specific enolase (NSE), S100β protein, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
Results. The success rate of VR-MCT course was 43%; 21 of 49 patients did not show POCD according to the established criteria at 11-12 days after CABG. Patients with successful VR-MCT showed improvements in attention (p=0,034) and short-term memory (p=0,016) compared with patients with unsuccessful training in the early postoperative period. In patients with successful VR-MCT, peripheral blood BDNF levels before surgery (p=0,029) and 1-2 days after CABG (p=0,04) were significantly higher compared to patients with unsuccessful training. We established factors specifying the complex indicator of the neurodynamics domain in VR-MCT — educational level, intima-media thickness, patient age, number of trainings and S100β protein level on day 1 after surgery (R2=0,38, F (5,43)=8,32, p<0,001); the attention domain — patient age, educational level, initial BDNF concentrations, both at the first day and on the first day. Peripheral blood S100β protein concentration and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) scores were assessed (R2=0,52, F (6,42)=10,76, p<0,001); for the short-term memory domain, the patient's age and baseline BDNF, NSE, and glucose concentrations were assessed (R2=0,37, F (4,45)=10,15, p<0,001).
Conclusion. The study results demonstrated that VR-MCT optimizes attention and short-term memory performance in patients with early POCD after on-pump CABG. Negative factors specifying cognitive status after VR-MCT include patient age, low education level, and baseline cognitive function, while protective factors include high perioperative BDNF concentrations and low peripheral blood concentrations of brain damage markers.
What is already known about the subject?
- Overweight patients have a higher risk of adverse cardiovascular events.
- Most overweight patients are at risk of coronary atherosclerosis and constitute the patient population undergoing interventional procedures or coronary artery bypass grafting.
- Overweight patients undergoing interventional coronary artery treatment require long-term rehabilitation in rehabilitation centers.
What might this study add?
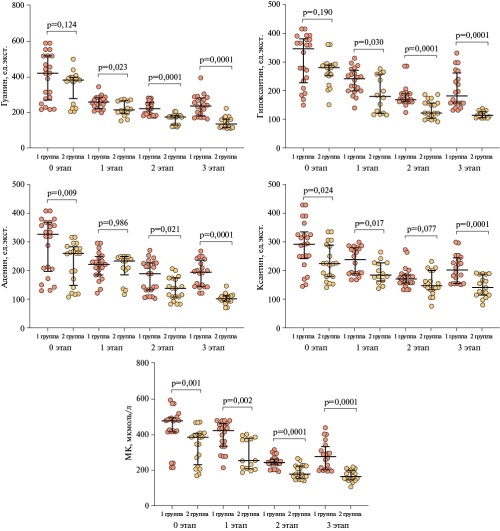
- In overweight patients following coronary artery bypass grafting, purine metabolite levels significantly increase in stage 3 of rehabilitation compared to stages 1 and 2, which indirectly suggests the resumption and progression of pathological process (ischemia, inflammation).
Aim. To study the purine metabolism changes in overweight patients who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) in the early postoperative period and during the rehabilitation, compared with that in patients with normal body weight.
Material and methods. This prospective study included 155 patients, including 87 (56%) men and 68 (44%) women, who underwent CABG due to critical coronary artery stenosis. All patients were diagnosed with single-vessel disease. The age range was 35-65 years. Patients were divided into 3 following groups: group 1 (n=85) — overweight patients; group 2 (n=70) — patients with normal body weight; group 3 (control group) — 30 healthy individuals. Changes in purine metabolite levels were assessed over time: 1 day after blood flow restoration at the cardiac surgery center, and then at rehabilitation stages 1 (1 to 3 months), 2 (3 to 6 months), and 3 (6 months to 1 year) at the cardiac rehabilitation center. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 27.0 and MedCalc version 22 software. The data are presented as tables and graphs using GraphPad PrismTM (version 7).
Results. In overweight patients after CABG, purine metabolite levels initially decrease, including in rehabilitation stages 1 and 2, and then sharply increase in rehabilitation stage 3.
Conclusion. In overweight patients, the level of purine metabolites increases sharply after CABG at rehabilitation stage 3 compared to those at stages 1 and 2, suggesting resumption of the pathological process (ischemia, inflammation).
COMORBIDITY
What is already known about the subject?
- The detection rate of obesity parameters in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease has a high variability across different diagnostic methods.
- At the same time, considering several available diagnostic criteria for osteosarcopenic obesity (OSO) is advisable.
What might this study add?
- We confirmed that body mass index is inadequate for diagnosing OSO, while the use of computed tomography has economic and medical limitations, and ultrasound does not provide information on skeletal muscles.
- Bioimpedance analysis may be considered as an alternative method for diagnosing OSO components.
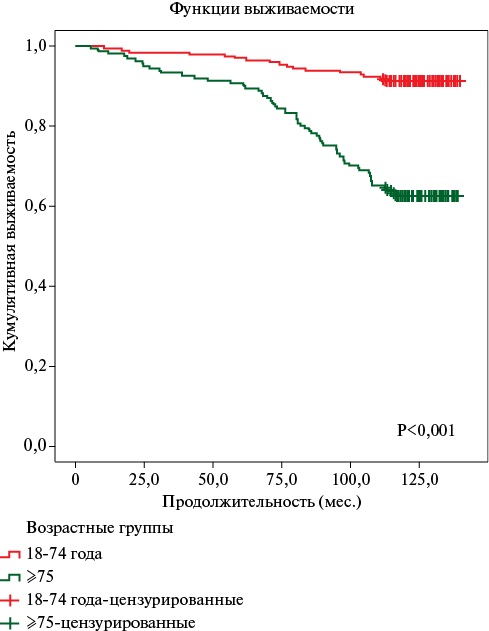
Aim. To analyze the incidence of osteosarcopenic obesity (OSO) using various fat depot indices in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease.
Material and methods. A total of 800 patients were included, with indices assessed after 12 months. Sarcopenia was diagnosed according to the criteria of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People (EWGSOP, 2019), and osteopenic syndrome was diagnosed according to World Health Organization (WHO, 2008) guidelines. Sarcopenia was screened using the SARC-F questionnaire, handgrip test, multislice computed tomography (CT) of muscle tissue, and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Body mass index (BMI) was assessed. Bioimpedance analysis, computed tomography, and adipose tissue ultrasound were performed. Statistical significance was considered at p≤0,05.
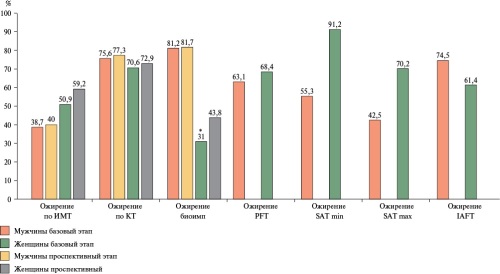
Results. A BMI >30 kg/m2 was more common at baseline in women (50,9%) compared to men (38,6%) (p=0,002), and in the prospective phase — 59,2% and 40,0%, respectively (p=0,001). Visceral fat values based on CT were higher in men, consistent with bioimpedance analysis and ultrasound findings. Subcutaneous fat thickness in women was higher than in men. Given the CT limitations and the inability to assess the musculoskeletal component using ultrasound, bioimpedance analysis can be used as an alternative diagnostic method for OSO.
Conclusion. The incidence of obesity depended on the diagnostic method and ranged from 38,7% to 81,2% in men and 31,0% to 91,2% in women. An analysis of the detection rate of visceral adipose tissue components revealed sex differences and variations in the studied indicator depending on the diagnostic method (from 2,0% for BMI to 16,4% for intraabdominal fat thickness).
STUDIES AND REGISTERS
What is already known about the subject?
- Coronary artery disease (CAD), especially in patients with multiple comorbidities, is associated with an unfavorable prognosis.
What might this study add?
- This study characterized groups of patients with CAD and identified the main factors influencing the risk of death and adverse events over a 10-year follow-up period.
- Groups of patients with CAD with the highest mortality during this period were described.
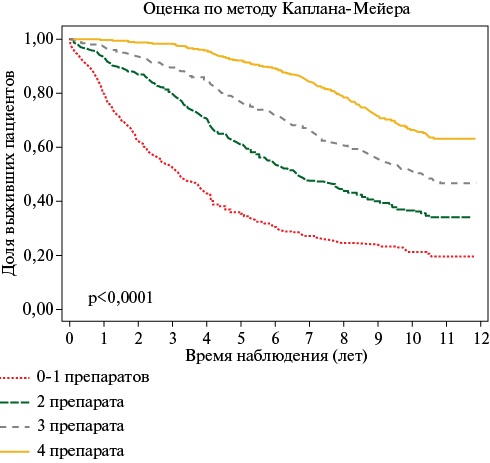
- We established that the use of complete quadruple pharmacotherapy (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers, β-blockers, statins, and antiplatelet /anticoagulant agents in the absence/presence of atrial fibrillation) is associated with a 3-fold reduction in all-cause death risk.
- In patients with CAD, frequent hospitalizations for CVD (>1 every two years) are associated with a higher death risk over 10 years, while less frequent hospitalizations are associated with a lower risk than in those who have not been hospitalized.
Aim. To evaluate outcomes over 10-year follow-up and the risks of adverse events in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) within an outpatient registry.
Material and methods. The RECVAZA outpatient registry, based at three clinics in Ryazan, included 2548 patients with CAD (age, 70,4±10,8 years; men, 28,5%). The following outcomes were assessed from 2012 to 2023 (follow-up period, 8,2±3,3 years): death, myocardial infarction (MI), cerebrovascular accident (CVE), and hospitalization for cardiovascular disease (CVD). Outcome information was obtained from medical records, surveys, and electronic databases.
Results. During 10-year follow-up, 1321 patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) died in the RECVASA registry, which is 51,8%. The main causes of death were CVD (44,4%) and cancer (8,8%). A particularly high proportion of deaths was observed among patients who, at the time of inclusion in the study, had prior stroke (71,9%) and MI (61,5%); a combination of CAD with hypertension (HTH), heart failure (HF) and atrial fibrillation (AF) (79%); age ≥80 years (91,7%). The highest all-cause and cardiovascular death risk was associated with age (hazard ratio (HR)=1,06 and HR=1,07; p<0,001); male sex (HR=1,70 and HR=1,62; p<0,001); prior CVE (HR=1,86 and HR=2,13; p<0,001); type 2 diabetes (HR=1,55 and HR=1,67; p<0,001); decreased hemoglobin level (HR=1,66 and HR=1,72; p<0,001); increased hemoglobin level (HR=1,63 and HR=1,92; p=0,005 and 0,004); smoking (HR=1,51; p=0,001 and HR=1,72; p=0,003), respectively. The risk of MI was most associated with male sex and prior MI (HR=1,77 and HR=2,61; p<0,001), while the risk of CVE — with AF and prior CVE (HR=1,65 and 3,78; p<0,001), with systolic blood pressure <110 mm Hg (HR=2,72; p=0,01). Hospitalization for CVD more than once every 2 years was associated with a higher death risk (by 1,6 times), but a lower rate — with a lower risk (by 1,9 times) than in its absence. When quadruple therapy was prescribed, including a renin-angiotensin system blocker, a beta-blocker, a statin, and an antiplatelet/anticoagulant agent in the presence/absence of AF, compared to those prescribed 0-1 of these, the all-cause and cardiovascular death risk was 3,5 and 4,2 times lower, respectively.
Conclusion. Over 10-year follow-up, 51,8% of patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) died. The highest mortality rate was observed in patients with prior MI and SVE, type 2 diabetes, a combination of CAD, HTN, HF, and AF, and low hemoglobin levels. Hospitalizations for CVD more than once every two years were associated with a higher death risk, but a lower hospitalization rate was associated with a lower risk than in patients with no cardiovascular hospitalizations. Prescription of quadruple therapy with a renin-angiotensin system blocker, a beta-blocker, a statin, and an antithrombotic agent, when indicated, reduced the all-cause and cardiovascular mortality risk by 3,5 and 4,2 times, respectively.
What is already known about the subject?
- The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in excess mortality (compared to the three pre-pandemic years).
- COVID-19 is associated with complications and aggravation of many noncommunicable diseases (NCDs).
- Data on the impact of obesity on the incidence, severity, and outcomes of COVID-19 are contradictory.
What might this study add?
- Confirmed COVID-19 was observed in 44% of patients with pre-obesity/obesity.
- Higher body mass index, prior myocardial infarction, and diabetes were associated with adverse outcomes in patients with pre-obesity/obesity.
- A third of these patients experienced progression of existing NCDs after COVID-19, and one in four patients developed a new-onset NCD.
- Adherent patients and older people were less at COVID-19 risk compared to with non-adherent and younger patients.
- After the end of the COVID-19 pandemic, a decrease in criticality in weight self-assessment criticality was noted, primarily in patients with pre-obesity.
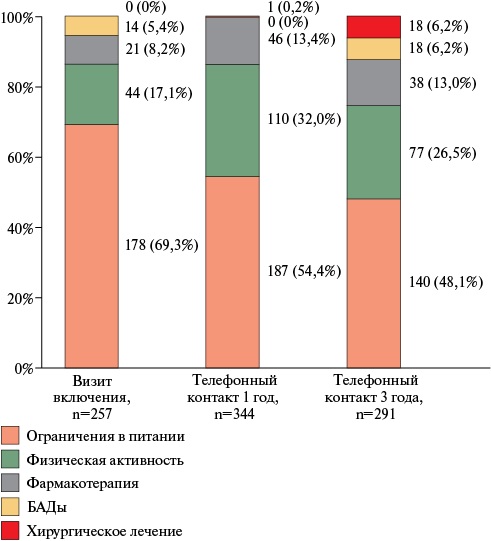
Aim. To evaluate the health status and outcomes of patients with overweight (pre-obesity) or obesity during long-term follow-up as part of the EVA observational program.
Material and methods. The EVA study included patients with overweight and obesity (body mass index (BMI) >25 kg/m2) from the outpatient registry of patients with cardiovascular diseases or their risk factors from April 8, 2019 to March 24, 2020. One and three years after the enrollment visit (coinciding with the COVID-19 pandemic), we contacted patients by telephone to collect information on body weight at the survey date, medication adherence, and subjective assessment of pre-obesity/obesity. At the three-year follow-up, data were collected on COVID-19 history and the changes of comorbid conditions during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Results. The study included 295 patients. The mean follow-up period was 3,6±0,5 years. The second telephone contact yielded following information on 261 (88,5%) patients: 18 — died, 243 — alive. In addition, 129 (43,7%) patients had COVID-19. Adherent patients and older people were less susceptible to the risk of COVID-19 infection compared to non-adherent and younger patients (p=0,016 and p=0,043, respectively). Every third (32,3%) patient who had COVID-19 experienced worsening of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), and almost every fourth (23,4%) patient developed new-onset NCDs. A decrease in weight self-assessment criticality was found, especially in patients with pre-obesity, 40% of whom considered their body weight to be normal. Predictors of adverse outcomes were prior myocardial infarction (hazard ratio (HR)=6,10; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1,18-31,46 (p=0,031)), type 2 diabetes (HR=2,78; 95% CI: 1,03-7,51, p=0,043) and BMI (HR=1,12; 95% CI: 1,01-1,24 (p=0,035)).
Conclusion. Significant predictors of an unfavorable prognosis in patients over a 3-year follow-up period were elevated BMI, prior myocardial infarction, and diabetes. After COVID-19, one-third of patients experienced progression of existing noncommunicable diseases, and one in four patients developed a new-onset NCDs.
Non-adherence was one of two factors associated with COVID-19 infection. During the COVID-19 pandemic, a slight decrease in weight self-assessment criticality was noted in patients with pre-obesity or obesity.
What is already known about the subject?
- Clinical trials often contain missing and incorrect data, which, if ignored, can lead to incorrect conclusions.
What might this study add?
- A specific example of a table with missing data from an acute coronary syndrome registry is provided. Russian acute coronary syndrome registries are analyzed for missing data and patients lost to follow-up.
This article presents information on missing and incorrect data in clinical trials in medicine and their impact on the results It describes the significance of lost to follow-up patients in prospective studies and individual missing data for a specific patient. An example of a database of the acute coronary syndrome (ACS) registry with missing data is given. The article also mentions the issue of fake data. It discusses various methods for filling in missing data in clinical registries and the main principles for preventing them. The article analyzes Russian ACS registris in terms of missing data and patients lost to follow-up.
CLINIC AND PHARMACOTHERAPY
What is already known about the subject?
- Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a universal hepatoprotective agent that can be used to treat hepatobiliary pathologies, as well as functional gastrointestinal disorders.
- UDCA also has the potential to influence metabolic parameters and can be used in the primary prevention of atherosclerosis and associated complications.
What might this study add?
- The complex effects of UDCA on key metabolic risk factors make it possible to be recommended for inclusion in the treatment of not only non-alcoholic fatty liver disease but also other metabolic diseases to reduce cardiovascular risks.
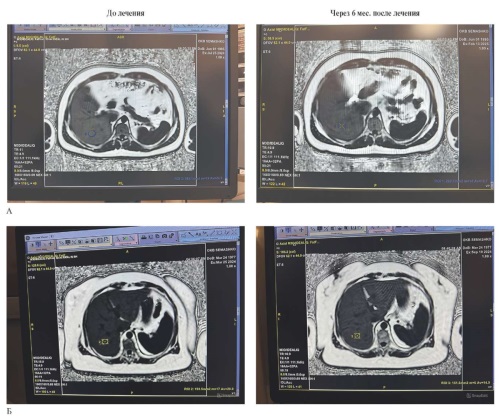
Aim. To evaluate the efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA, Ursosan) in the complex treatment of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) based on abdominal magnetic resonance imaging data and its effect on metabolic cardiovascular risk factors.
Material and methods. This prospective, open-label, non-randomized study was conducted involving 53 patients with NAFLD. Subjects were divided into two groups. All patients were assigned to a hypocaloric diet and moderate physical activity. Patients in the first group received UDCA at a dose of 12 mg/kg of body weight per day for 6 months. Patients in the second group (the comparison group) did not receive medication and followed lifestyle modification recommendations. The study included clinical and laboratory examinations, including abdominal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging to determine liver fat fraction, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, blood glucose, uric acid, and lipid profile levels. Statistical analysis was performed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Spearman correlation analysis.
Results. Ursosan therapy resulted in a significant decrease in liver fat fraction (median from 11,4 to 9,2%; p=0,009), total cholesterol (from 6,6 to 5,3 mmol/L; p=0,001), triglycerides (from 1,9 to 1,6 mmol/L; p=0,010), uric acid (from 386 to 334 μmol/L; p=0,001), alanine aminotransferase (from 28,1 to 23,0 U/L; p=0,020), and aspartate aminotransferase (from 25,3 to 22,6 U/L; p=0,021). No side effects were observed.
Conclusion. Ursosan has a comprehensive hepatoprotective effect, which helps slow the progression of liver steatosis. UDCA reduces total cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which is important for the prevention of atherosclerosis. By improving metabolic processes, purine, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism is normalized, which contributes to an improved metabolic profile. The safety and efficacy of UDCA allow it to be included in the complex therapy of not only NAFLD but also other metabolically associated diseases.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about the subject?
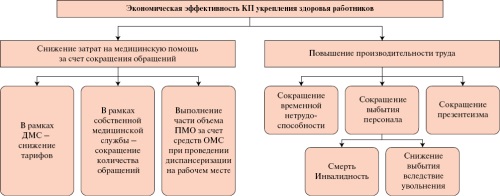
- Workplace wellbeing programs play a crucial role in maintaining employee health, increasing their work productivity, and improving overall economic performance of the organization and the state as a whole.
- Researchers evaluate economic efficiency using a variety of methods and indicators, and research results can be mixed and depend on many factors, such as industry specifics, organization scale, program duration, and calculation methodology used.
What might this study add?
- Despite favorable findings from several studies, the absence of a unified approach to evaluating the economic efficiency of workplace wellbeing programs necessitates the development of a methodological framework tailored specifically for Russian organizations, taking into account the relevance of this direction within the national project "Long and Active Life".
Workplace wellbeing programs are a crucial reserve for increasing life expectancy and ensuring national economic security. Therefore, this area is in focus of state policy, which has been reflected, among other things, within the National Project "Long and Active Life". However, there is a noted lack of methodological approaches to determining the economic efficiency of workplace wellbeing programs. This hampers an increase in coverage of working population with preventive measures, since economic arguments are necessary to enhance employers' motivation to invest in employees’ health. This review presents methods for assessing the economic effectiveness of workplace wellbeing programs used by organizations in foreign countries, whose results may be ambiguous. Given the development of methodical base for strengthening health at workplaces, including those within the National Projects, the authors present herein rationale for developing methodology on economic efficiency of workplace wellbeing programs, as well as outline future methodology framework.
What is already known about the subject?
- Twenty-hour blood pressure monitoring (BPM) is an informative diagnostic method that provides objective and comprehensive information about a patient's blood pressure.
- Twenty-hour BPM, developed as a method for measuring blood pressure in a patient's usual setting (outside the clinic), is increasingly being used in hospital examinations.
What might this study add?
- Literature data shows that in real-world clinical practice in Russia, average 24-hour systolic and diastolic blood pressure values obtained by inhospital 24-hour BPM are, on average, lower than those obtained during ambulatory BPM.
- Inhospital 24-hour BPM is more often performed in younger individuals with hypertension and fewer cardiovascular comorbidities.
- Inhospital 24-hour BPM parameters retain their prognostic value, including their association with the all-cause mortality risk.
Twenty-hour blood pressure monitoring (BPM) has become widely used in modern practice. This method, originally designed to obtain information on blood pressure levels in a patient's usual environment (outside the hospital), is increasingly being used for inpatient care. Particularly, this is a part of compulsory health insurance screening programs for patients with hypertension (HTN) and other cardiovascular diseases. Although the inpatient BP profile for the same patient may differ from that observed in outpatient settings, inhospital 24-hour BPM retains many of the advantages described for outpatient use, including the objectivity of results and the prognostic value of the data obtained.
The purpose of this article is to critically analyze studies (including the authors' ones) related to inhospital 24-hour BPM. The work is supplemented by some original author’s results, reflecting the typical characteristics of patients who most frequently undergo monitoring in hospital settings, as well as the prognostic value of inhospital 24-hour BPM parameters.
What is already known about the subject?
- As part of the World Health Organization's priority areas for reducing noncommunicable disease mortality by 2% per year globally, the idea and goal of a tobacco endgame have been formulated — a complete end to the tobacco epidemic.
- Tobacco endgame policy initiatives include product-focused, consumer-focused, market/supply-focused, and institutional strategies.
What might this study add?
- Most countries with tobacco endgame goals are implementing market- and supply-focused strategies, although not fully.
- Institutional strategies are aimed at countering tobacco company interventions to achieve tobacco endgame goals, but there are no publications demonstrating their implementation and/or effectiveness.
This article is the next part of a study on tobacco endgame strategies and measures. It analyzes market- and supply-side policy initiatives, institutional initiatives, the corresponding strategies and measures within these initiatives, and their effectiveness.
What is already known about the subject?
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a disease with a high risk of sudden cardiac death.
- Circulating microRNAs are potential biomarkers of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
What might this study add?
- Current studies investigating the profile of circulating microRNAs in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy are characterized by significant methodological heterogeneity, making it difficult to directly compare data and draw definitive conclusions.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a common inherited heart disease and a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young adults. Recently, an increasing number of studies have been published examining the role of microRNAs in the regulation of key pathological processes in HCM, such as myocardial fibrosis, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, and cardiac remodeling. The aim of this review is to analyze recent original studies analyzing the potential of circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for diagnosis and risk assessment in patients with HCM.
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)