ADDRESS TO THE READERS
ISCHEMIC HEART DESEASE AND MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
What is already known about the subject?
- Identification of patients with transient myocardial ischemia due to obstructive coronary artery disease (CAD) is an important clinical task.
- It is for this type of chronic coronary syndrome that there are interventions that can positively affect the prognosis.
What might this study add?
- The presence of obstructive CAD can be predicted using detailed characteristics of dyspnea, anxiety-depression assessment scales, history data, electrocardiography, echocardiography parameters.
- The following indicate the presence of obstructive CAD: longer duration and severity of dyspnea, low anxiety-depression scale scores, no left ventricular diastolic dysfunction as assessed by e'lateral (early diastolic mitral annular velocity along the left ventricular lateral wall).
Aim. To characterize the potential of assessing the probability of obstructive coronary atherosclerosis in patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) and paroxysmal dyspnea due to myocardial ischemia.
Material and methods. In a cross-sectional study of 36 stable patients with CAD, complaining of paroxysmal dyspnea during stress echocardiography, transient myocardial ischemia was detected. According to coronary angiography data, coronary artery stenosis ≥50% was detected in 30 (83,3%) of them: ≥70% — in 25 (69,4%), ≥90% — in 18 (50,0%) patients.
Results. Independent parameters associated with stenosis ≥50% were a lower anxiety-depression scale score, the presence of pathological Q waves and higher e'lateral (early diastolic mitral annular velocity along the left ventricular lateral wall); for ≥70% — no bendopnea, greater duration and severity of dyspnea, a history of coronary stenting, no prior paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and a higher e'lateral; for stenosis ≥90% — greater severity of dyspnea, lower scores on the visual analogue scale of depression and greater e'lateral. The area under the characteristic curve when predicting stenosis ≥50% was 0,81 for the regression equation and 0,68 for the point scale, while ≥70% — 0,91 and 0,71, ≥90% — 0,82 and 0,75, respectively.
Conclusion. The most informative indicators of obstructive CAD in the studied patients were a longer duration and severity of dyspnea, a low anxiety-depression scale score, as well as the absence of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction.
АТЕРОСКЛЕРОЗ И ФАКТОРЫ РИСКА
What is already known about the subject?
- Cross-sectional studies have demonstrated associations between vascular wall parameters and bone mineral density (BMD).
- Currently, there are isolated prospective studies confirming the stability of associations or the relationship between preclinical parameters of atherosclerosis and osteoporosis.
What might this study add?
- Vascular stiffness, subclinical atherosclerosis, and BMD parameters in postmenopausal women change over a 10-year period.
- A relationship has been demonstrated between the augmentation index, intima-media thickness, the presence of atherosclerotic plaques, and BMD, which may play an important role in prognosis and prevention.
Aim. To study the relationships between vascular wall parameters and bone mineral density (BMD) over a 10-year period.
Material and methods. The study included 93 menopausal women without clinical manifestations of atherosclerosis at the baseline stage, who underwent outpatient examination twice with an interval of 10 years. Measurement of pulse wave velocity and augmentation index (AI) using applanation tonometry, carotid ultrasound to determine the intima-media thickness (IMT) and register plaques, and measurement of BMD using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry were performed at both visits.
Results. Over a 10-year period, an increase in AI, IMT, and plaque count (p<0,001) and a decrease in BMD were noted in the femoral neck and proximal femur (p<0,001), but not in the spine. Multivariate regression analysis adjusted for factors identified at the baseline visit (age, postmenopause duration, body mass index, hypertension, and cardiovascular and osteoporosis therapy) showed that AI, IMT, and plaque presence independently contributed to the decrease in bone mass. Pulse wave velocity and the number of atherosclerotic plaques did not act as independent factors in the decrease in BMD.
Conclusion. Over a long period of time, a stable negative association was maintained between AI, IMT, the plaque presence, and bone mass, which did not depend on fracture and cardiovascular risk factors, as well as the use of antiresorptive and cardiovascular therapy.
OBESITY
What is already known about the subject?
- In the world, >1 billion people had obesity, or every eighth inhabitant of the planet. From 1990 to 2022, the incidence of obesity has doubled.
- The frequency of overweight in the Russian population is 44,0% among men and 33,7% among women, while obesity — 30,0 and 39,5%, abdominal obesity — 30,9 and 55,1%, respectively.
What might this study add?
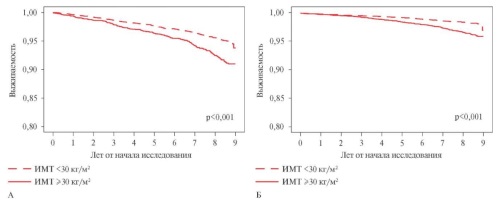
- The presence of obesity, including abdominal obesity, significantly worsens survival in the Russian cohort among both men and women.
- The associations of body mass index and all-cause death risk in the Russian cohort are U-shaped, while the lowest all-cause death risk is shifted towards overweight. However, the risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular events increases as the body mass index increases.
Aim. To study the contribution of obesity, including abdominal obesity (AO), to the risk of all-cause death and cardiovascular events (CVE) in the Russian population.
Material and methods. The representative samples of the Russian population aged 25-64 years from the ESSE-RF (2012-2014) and ESSE-RF2 (2017) studies were analyzed (n=22869). A modular questionnaire and standard epidemiological methods for assessing risk factors were used. The body mass index (BMI) was calculated using the following equation: BMI=body mass (kg)/height (m2). Overweight was defined as 25,0≤ BMI ≤29,9 kg/m2, while obesity — as BMI ≥30,0 kg/m2, and AO — as waist circumference ≥102 cm in men and ≥88 cm in women. High blood pressure (BP) was defined as systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP ≥90 mm Hg. The presence of diabetes with type indication was assessed by a questionnaire. In this analysis, carbohydrate metabolism disorders were defined as fasting glucose ≥6,1 mmol/l and/or a history of diabetes. The prospective observational cohort was formed from 14 regions included in ESSE-RF and ESSE-RF2. Every 2 years, the following were assessed: causes of death, non-fatal CVD, new cases of cardiovascular diseases and cardiovascular events. Statistical analysis was performed using the statistical programming language and the R environment (version 4.1) with open source code. To assess survival, Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used with the log-rank test with Holm's adjustment. Associations with endpoints were assessed using Cox models. The differences for all tested hypotheses were considered significant at p<0,05.
Results. The presence of obesity, including AO, significantly worsens survival in the Russian cohort (p<0,001), and is also significantly associated with fatal and non-fatal CVD (p<0,001). The significance of obesity is preserved in multivariate analysis adjusted for sex, age and region of residence. The lowest all-cause death risk is shifted towards overweight. The risk of fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular diseases increases with increasing BMI. In the Russian cohort, the combination of obesity with carbohydrate metabolism disorders and elevated blood pressure significantly worsens the prognosis (p<0,001) compared to each condition separately.
Conclusion. Obesity, including AO, is associated with worsening survival in the Russian population. Despite the obesity paradox, in which the lowest all-cause death risk is shifted towards overweight, the risk of CVD increases with increasing BMI in the Russian cohort. To control obesity, it is important to improve the detection of obesity, including through medical check-ups and preventive examinations, as well as the choice of treatment tactics for obese patients according to clinical guidelines.
What is already known about the subject?
- One of the significant comorbidity factors is obesity.
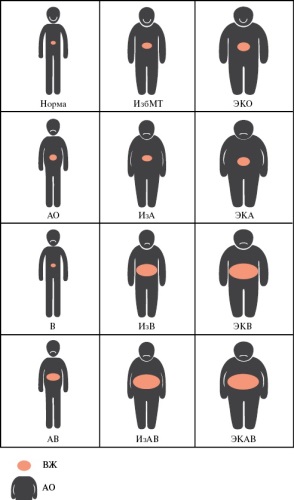
- Studies of different types of obesity, highlighting phenotypes with regard to visceral fat estimation, improve the understanding of the relationship between adipose tissue and comorbid diseases.
What might this study add?
- In young and middle-aged individuals with BMI ≥25 kg/m2 and/or abdominal obesity, obesity multimorbidity is associated with age ≥32 years and visceral fat ≥7 units. This group of patients should be prioritised for obesity-related polypathy.
Aim. To assess the characteristics of comorbid obesity diseases and polypathies in young and middle-aged individuals taking into account the obesity phenotype.
Material and methods. This cohort cross-sectional study was used to examine 201 patients with a body mass index (BMI) ≥25 kg/m2 and/or abdominal obesity (AO) (median age 39 [33-47] years). Anthropometry was performed. Visceral fat (VF) level was measured using the bioelectrical impedance analysis. We analyzed participants for the following diseases/conditions comorbid with obesity: hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia, prediabetes, osteoarthritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), pancreatic steatosis, obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
Results. Dyslipidemia (77,6%), HTN (32,3%), prediabetes (25,4%), less often — osteoarthritis (21,9%), pancreatic steatosis (19,9%), NAFLD (16,9%), OSA (10,4%), gastroesophageal reflux disease (9,0%) were established in more than a quarter of cases. Obesity multimorbidity prevailed (83,1%), represented by combinations of HTN with prediabetes, NAFLD, pancreatic steatosis; HTN with prediabetes, OSA. Based on the decision tree, multimorbidity was most common among individuals aged ≥32 years with a VF ≥7 units. Therefore, an algorithm was developed to prioritise screening for polypathy of obesity related comorbidity.
Conclusion. With a phenotype of BMI ≥25 kg/m2, AO and an increased VF level, there is a high probability of HTN, NAFLD, and pancreatic steatosis. Obesity multimorbidity was diagnosed in every eighth patient. The highest probability of ≥3 comorbid obesity diseases was observed in individuals with a BMI ≥25 kg/m2 and/or AO at the age of ≥32 years and VF ≥7 units.
What is already known about the subject?
- In Russia, about a quarter of the adult population suffers from obesity, which makes the problem relevant for the healthcare system.
- Obesity is a significant independent risk factor for cardiovascular diseases.
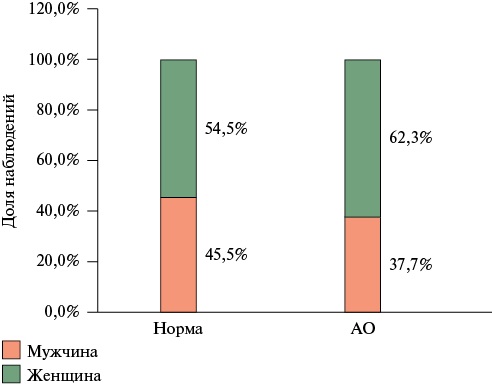
- Obesity and abdominal obesity are significantly more common in women than in men. In addition, women have a higher prevalence of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, which may be associated with fat tissue distribution characteristics and requires further study.
What might this study add?
- For the first time in Russia, gender-specific features of myocardial remodeling and the nature of fat tissue distribution depending on sex in patients with class 1 obesity without cardiovascular diseases have been demonstrated.
- Women are more likely to have left atrial dysfunction, expressed in a longitudinal strain decrease in the reservoir phase, which is due to more pronounced visceral obesity, including epicardial one.
Aim. To conduct a comparative analysis of the adipose tissue (AT) distribution and left myocardial geometry and functional parameters in women and men with class 1 obesity without previously diagnosed cardiovascular diseases.
Material and methods. The analysis included 88 patients with class 1 obesity aged 25-50 years who had no history of cardiovascular and non-communicable diseases. Depending on sex, the subjects were divided into 2 groups. In each group, the structural and functional cardiac parameters were assessed, including longitudinal strain indices and AT distribution. The studies were performed on a Philips EPIQ CVx 2D ultrasound system by one specialist.
Results. Women had higher absolute (49,0 [41,0;57,5] vs, 44,0 [37,0;54,0] ml, p=0,076) and indexed left atrial (LA) volumes (18,3 [14,6;20,1] vs 14,7 [12,0;17,2] ml/m2, p=0,015) than men, as well as a higher left ventricular mass index (42,2 [37,2;47,8] vs 33,0 [31,3;41,1] g/m2,7, p=0,001). Men had higher left atrial strain during reservoir phase (LASr) (p=0,047) than women, whereas women were more likely to have LA dilation (30 vs 10%, p=0,001). In men, the probability of an increase in LA size was 5,2 times lower than in women (odds ratio (OR) 0,192; 95% confidence interval: 0,068-0,541, p=0,002). Women had a significantly higher probability of a decrease in LASr (OR 3,2, p=0,022), which may be associated with specifics of visceral AT, including epicardial, distribution.
Conclusion. Women are more likely to have LA dysfunction, which is probably due to the greater severity of visceral obesity. The established relationship with epicardial AT thickness confirms the importance of its assessment in the standard echocardiographic protocol. The results obtained suggest that weight loss, especially in women, should be a priority for the prevention of cardiovascular events.
ФАКТОРЫ РИСКА
What is already known about the subject?
- Most epidemiological studies register a significant increase in the risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in hyperuricemia.
What might this study add?
- In the present study, an increase in the serum uric acid level itself was not associated with adverse cardiovascular events.
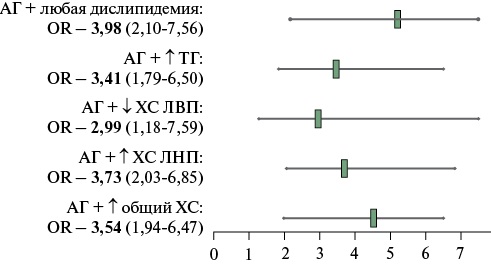
- Only when hyperuricemia is combined with hypertension or individual forms of lipid profile disorders, a significant association with some types of cardiovascular events was revealed.
Aim. To assess the association between hyperuricemia (HU), as well as its combination with hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia and cardiovascular events.
Material and methods. This retrospective analysis included a representative sample of 1603 residents of Krasnoyarsk Krai aged 25-64 years from the Russian epidemiological study ESSE RF. Uric acid >360 μmol/l was taken as the HU criterion. Statistical processing included logistic regression with sequential exclusion of insignificant factors to search for associations between HU, HTN and lipid metabolism disorders with cardiovascular events — stroke, myocardial infarction (MI) and coronary artery disease (CAD).
Results. The prevalence of HU was 34,6%, among men — 47,6%, among women — 26,1%. No significant differences in the frequency of MI, stroke and CAD among individuals with and without HU were found. Regression model revealed a significant increase in the risk of stroke (odds ratio (OR) 5,7; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1,68-19,34) and CAD (OR 4,99; 95% CI: 2,73-9,09), but not MI, as well as stroke (OR 2,95; 95% CI: 1,31-6,64) (p=0,009), but not MI and CAD, when HU was combined with HTN.
Conclusion. No significant association was found between HU and cardiovascular events. However, the combination of HU with HTN, as well as HU with low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, was significantly associated with stroke and CAD.
ПРИВЕРЖЕННОСТЬ ЛЕЧЕНИЮ
What is already known about the subject?
- High-quality outpatient care for patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction can significantly improve the course of the disease and prognosis.
- Complete adherence of patients to drug therapy is the most important condition for its effectiveness.
What might this study add?
- More than half (60%) of patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction took ≥5 medications.
- Almost a quarter (22,2%) of all patients included in the study violated the drug regimen prescribed by the physician.
- The main reasons for incomplete adherence to treatment were forgetfulness and insufficient medical awareness of patients.
Aim. To assess the clinical features and adherence to treatment in outpatients with heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Material and methods. This cross-sectional observational study was conducted based on a city outpatient clinic involving 230 patients >60 years old with HFpEF. Adherence to therapy was assessed using the National Society for Evidence-Based Pharmacotherapy scale.
Results. The mean age of the subjects was 74 years (women, 60,4%). Multimorbidity was recorded in 99,1% of patients, while the most common comorbidities were hypertension (97,4%), coronary artery disease (65,7%) and obesity (39,1%). Most patients (57%) belonged to New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class II. The median value of the left ventricular ejection fraction was 64%; 60% of respondents took ≥5 drugs. The level of complete adherence to therapy (0 points) was demonstrated by 77,8% of patients. Among the reasons for incomplete adherence (≥1 point), forgetfulness dominated (54,9%), followed by doubts on the need for therapy (15,7%) and complexity of the treatment regimen (11,8%).
Conclusion. Despite the high level of complete adherence to treatment found in the majority of patients with HFpEF, 22,2% demonstrated various violations of the drug treatment regimen, which requires close attention from outpatient physicians.
INTERDISCIPLINARY PROBLEMS IN CARDIOLOGY
What is already known about the subject?
- Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a systemic connective tissue disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach to patient management.
- Cardiac autonomic dysfunction (CAD) is a potential cause of sudden cardiac death in patients with SSc.
What might this study add?
- Patients with SSc who do not have cardiovascular diseases show early signs of CAD.
- The COMPASS-31 questionnaire and the 30:15 clinical test can be used in patients with SSc by a primary care physician for early diagnosis of CAD and referral to a cardiologist for additional examination and possible risk stratification of sudden death.
Aim. To study the potential of early diagnostics of cardiac autonomic dysfunction (CAD) in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc).
Material and methods. The case-control study included 41 patients with SSc and 19 healthy individuals. Clinical tests (deep breathing test, blood pressure and heart rate (30:15) response to the orthostatic test) were performed, and patients were surveyed using the Composite Autonomic Symptom Score-31 (COMPASS-31) questionnaire.
Results. The total COMPASS-31 score in patients with SSc was 24,6 [13,6; 37,6], in the control group — 13,8 [2,7; 32,8] (p=0,021). The combination of vasomotor and orthostatic disorders was observed more often in patients with SSc than in the control group — in 23 (56,1%) and 3 (15,8%) participants, respectively (OR — odds ratio) =6,82; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1,72-27,06; p=0,003. In patients with SSc, the 30:15 ratio (heart rate response to orthostatic test) was significantly lower than in the control group (p=0,001); pathological test results indicating CAD were more often observed in patients with SSc (OR=6,50; 95% CI: 1,26-33,58; p=0,016). A positive correlation was found between the total COMPASS-31 score and the duration of SSc from the disease onset, diagnosis, and the duration of Raynaud's syndrome (R=0,39, R=0,35, R=0,38, p<0,05).
Conclusion. Patients with SSc show following early signs of CAD: vasomotor and orthostatic disorders are recorded 6,8 times more often according to the COMPASS-31 questionnaire, and pathological results of the 30:15 clinical test are detected 6,5 times more often.
CLINICAL CASE
- Treatment of electrical storm is aimed at eliminating the pathophysiological mechanisms of its development.
- The main stages include diagnosis, relief and prevention of repeated episodes of electrical storm, as well as solving key problems in patients with end-stage heart failure.
Electrical storm (ES) is a potentially life-threatening condition, the incidence of which increases with the number of patients with implantable cardioverter-defibrillators. One of the common causes of its development is coronary artery disease. Stopping ES is a complex task that requires the participation of a multidisciplinary team. This case report describes successful treatment of ES in a patient with heart failure of ischemic origin with a left ventricular ejection fraction of 19%, severe myocardial scarring, and a chronic left ventricular apex aneurysm. The patient developed multiple (up to 25/day) episodes of hemodynamically stable, symptomatic, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with myocardial scarring.
REVIEW ARTICLES
What is already known about the subject?
- Individuals diagnosed with familial hypercholesterolemia are classified as having a high or very high risk of cardiovascular disease.
- MicroRNA (small non-coding ribonucleic acids) are involved in all stages of atherogenesis — from endothelial dysfunction to plaque rupture.
What might this study add?
- Studies on the analysis of expression levels of various microRNAs in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia differ greatly methodologically, which makes it difficult to compare the results obtained with each other.
- The main differences between the studies are the comparison groups, the type of biological material, the method for determining microRNAs, and the statistical analysis of the data obtained.
The most common inherited form of dyslipidemia and the main cause of premature cardiovascular disease is familial hypercholesterolemia. This disease is characterized by high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and, as a consequence, early coronary atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. Modern research increasingly focuses on the role of small non-coding ribonucleic acids (RNA), in particular microRNA, in the regulation of lipid metabolism and the development of atherosclerotic changes. The aim of this review was to analyze recently published studies describing the potential role of microRNA in assessing cardiovascular risk in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia.
What is already known about the subject?
- The skin microcirculation has a complexly organized, 3-link structure.
- There are a large number of methods for non-invasive study of human skin microcirculation.
What might this study add?
- An assessment of the diagnostic potential of three different research devices is given, taking into account the physical principles of their operation, which, based on skin microcirculation angioarchitectonics, allow obtaining physiological information from each link of microvascular bed.
- We described modern portable versions of all three types of devices that have appeared over the past 5-8 years, which allows to significantly expand the capabilities of researchers in remote microcirculation monitoring.
- A new diagnostic approach of human skin microcirculation study is briefly described, which does not require specialized medical equipment and is based on a standard webcam.
The aim of this descriptive review is to analyze the current state and further development of a new direction in functional diagnostics — non-invasive study of human skin microcirculation. The review considers the most frequently used non-invasive methods for research studying human skin microcirculation. The diagnostic potential of various devices is assessed taking into account the physical characteristics of their functioning and the skin microcirculation angioarchitectonics. The article considers the main directions of improvement of computer videocapillaroscopy, laser Doppler flowmetry and photoplethysmography methods, which are based on modern computer technologies and microelectronics. The main trends in this direction are miniaturization of devices, remote data transmission and the use of modern methods of automatic data analysis. A completely new method of obtaining physiological information is the analysis of a video plethysmography records using a conventional webcam. The method is based on the analysis of changes in the contrast of pixels during video recording of the skin surface, where the transitional capillary zones are located, blood flow changes in which lead to a change in the contrast of the pixels recorded by a standard webcam.
What is already known about the subject?
- Endothelial dysfunction (ED) is a pathological condition in which the balance of synthesis of various biologically active substances by endothelial cells is disturbed, characterized by hyperproduction of vasoconstrictors, prothrombotic and proinflammatory factors. This condition is a key link in the development of many noncommunicable diseases, including atherosclerosis, hypertension, heart failure and type 2 diabetes.
- ED often precedes the onset of clinical symptoms of diseases, making it an early diagnostic marker of vascular stiffness.
What might this study add?
- Further study of ED pathogenesis may contribute to a personalized approach to the development of novel ED markers reflecting vascular stiffness.
For many years, cardiovascular diseases remain the leading cause of death in the world. The most significant risk factor for their development is hypertension. Endothelial dysfunction is one of the central links in the pathogenetic mechanisms of the formation and progression of vascular stiffness in hypertension. That is why the identification and assessment of endothelial function is of high practical importance for practitioner.
The review aim is to analyze and summarize the available data on paraclinical diagnostics of endothelial dysfunction involved in the formation of vascular stiffness.
EXPERTS’ CONSENSUS
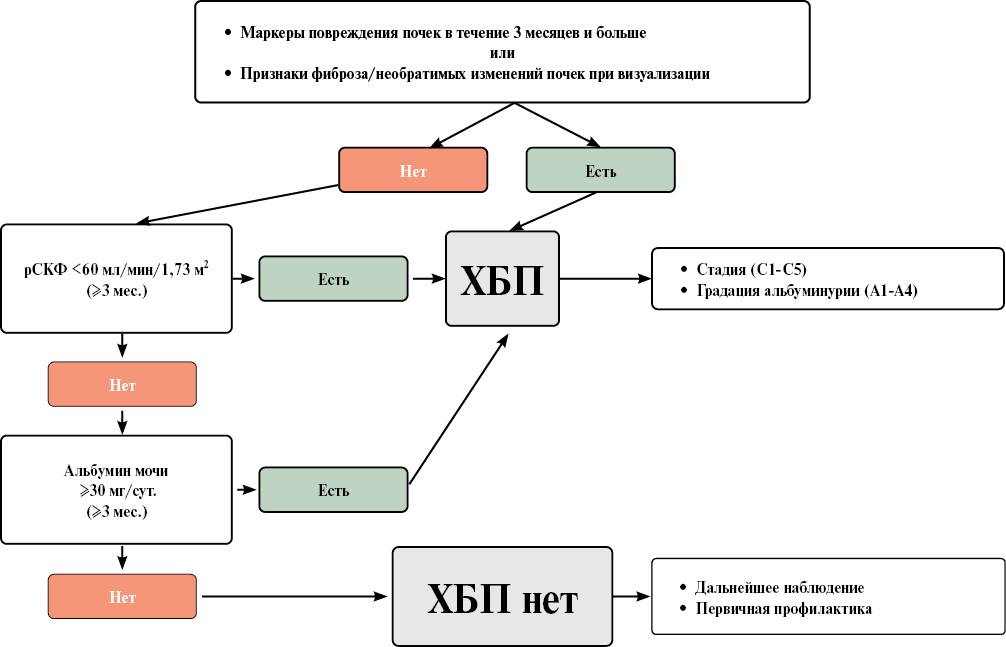
The consensus was developed by experts from the Russian Scientific Medical Society of Internal Medicine, the Russian Society for the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases, the National Nephrology Association, the Professional Nephrology Association, the Russian Society of Cardiology, the Russian Medical Society for Arterial Hypertension, the Heart Failure Society, the National Atherosclerosis Society, the Russian Endocrinology Association, and the Russian Gerontology and Geriatrics Association.
The expert consensus opinion was compiled on the basis of the relevant sections of national and international clinical guidelines on chronic kidney disease, prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis, hypertension, diabetes and heart failure.
ISSN 2619-0125 (Online)